

Determining the UPS (uninterruptible power supply) battery configuration using a formula can be quite complicated and, since many users are not very familiar with it, a more simplified method can be used to speed up the process and thereby save time.
This is typically done in the pre-planning phase before designing the practical application solution. The battery configuration can be quickly and simply calculated based on the UPS output load and the required backup time. The formula is as follows:Required battery capacity (Ah) = UPS capacity (kVA) x 109 (Ah/cell) + kVA + number of battery blocks per group
Example 1
As an example, consider a 130 V d.c. system of 120 kVA operating a UPS with 32 cells in series per bank, and requiring a backup time of 60 minutes. The required battery capacity is:
120 kVA x 109 Ah (cell/kVA) = 13 080 Ah (total requirement)
13 080 Ah / 32≈409 Ah
Therefore, if using a 12 V, 100 Ah battery bank x 4, there is a choice between using 32 cells per group, in which case the actual backup time will be less than 60 minutes, or 33 cells per group, resulting in a backup time of slightly more than 60 minutes.
If the required backup time is 30 minutes, then:
120 x 109 = 13 080 Ah
13 080 / 32≈409 Ah (for 60 minutes)
409 / 2≈205 Ah
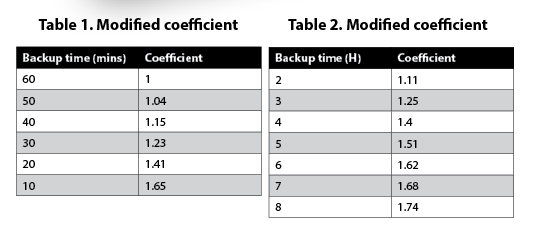
However, since the discharge power and discharge time of the battery are not linear, simply dividing by 2 is incorrect; rather, a modified coefficient must be used (see Table 1). Therefore, in this case, 205 x 1,23≈252 Ah, so one option could be 4 banks (32 cell/bank) of 12 V, 65 Ah battery.
If the backup time requirement is 20 minutes, then:
120 x 109 = 13 080 Ah
13 080 / 32≈409 Ah (for 60 minutes)
409 / 3≈136 Ah
136 x 1,41 (modified coefficient) 192 Ah
Therefore, one option could be 3 banks (32 cells/bank) of 12 V, 65 Ah batteries.
Example 2
Consider a 126 Ah/cell/kVA system, of 120 kVA UPS with 32 cells per bank. If the required backup time is more than one hour you also need to consider the modified coefficient in the calculation (see Table 2).
If the required backup time is 3 hours, then:
126 x 120 = 15 120 Ah
15 120 / 32≈472 Ah
472 x 3 = 1 416 Ah (for 3 hours)
Then divide it by a modified coefficient as 1 416 / 1,25≈1 133 Ah
The option of 4 banks of 12 V, 300 Ah batteries can therefore be selected.
According to the principle of energy conservation, the above method is the same for three-phase/single-phase or single-phase/single-phase UPS. Generally, high-power UPS systems are equipped with 32 batteries per battery pack and the number of parallel batteries should not exceed 4 so as not to affect the current sharing and charging effect of the battery pack.
However, the above is a simplified method that is only a rough calculation where the result which is not completely accurate. To obtain a more accurate result, one will also need to consider the parameters of the equipment, the requirements of the application, the power grid condition and the power conversion efficiency.
For more information contact Forbatt SA, +27 11 469 3598, [email protected], www.forbatt.co/index.php
| Tel: | +27 11 469 3598 |
| Fax: | +27 11 469 3932 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.forbatt.co |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Forbatt SA |
© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved