

The electronic components industry remains a major focus for many established companies with reputable design teams.
Emerging companies may face greater challenges when it comes to designing a scalable solution which incorporates their envisaged product from conceptualisation to high-volume production.
As a result, many of these emerging types of businesses are moving more into a role of integrating finished products to offer a working system for their customers, as opposed to going through the entire design phase only to find out from their end customer, towards the end of the design cycle, that a product may no longer be viable to bring to market for any number of reasons.
A typical system may comprise of a monitoring or controlling device communicating to backend hardware, with that backend device relaying information to a graphical interface for the end customer to use, as shown in Figure 1.
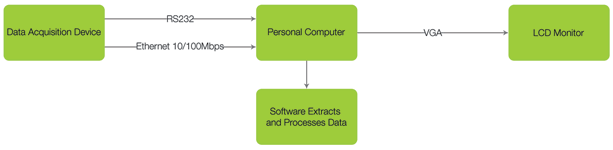
South Africa faces challenges which may not be present in other countries where a product has been designed. In particular, cable theft poses a major obstacle to designers as the communication link is often the backbone of a working system. The failure of this link in certain applications often results in complete failure of the system.
Permanent installations involving cabling are also becoming less and less attractive as a result of business needs changing and developing with technology. Despite these constraints, the demand for real-time monitoring and control systems is on the rise.
Otto Wireless Solutions, in association with WLINK, has introduced a range of industrial machine-to-machine (M2M) 3G and LTE routers with both LAN and Wi-Fi capability, to cater for these growing needs. By introducing these routers into the scenario presented earlier, the system could be transformed into a more efficient and modern system such as the one in Figure 2.
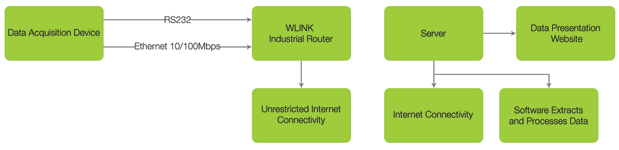
The immediate consequences of this alternative solution should be 1) there no longer exists a need for an external display device as the user’s personal computer or smartphone becomes the interface; and 2) for one data processor server there can be multiple remote data acquisition devices reporting to it, removing the need for a robust processor at every site.
The WLINK range of industrial routers supports all the South African mobile networks’ HSPA+ technology (21 Mbps) and the 4G models support the Vodacom and MTN LTE networks (100 Mbps). The top of the range model boasts a dual-SIM feature to enable switching between two different SIM cards – most commonly based off different networks to increase the reliability of network coverage. For the single-SIM models, an ICMP and cellular traffic check feature ensures the router remains online as real-time response checks can be done via the networks.
To further add to the reliability of this communication link, all the WLINK routers support an M2M management platform,running on a Windows-based server, to which the remote routers report according to a pre-assigned schedule. These reports include the current public IP address of the router as well as the received signal strength.

These two indicators provide advanced usage with respect to remote management. Dynamic DNS is no longer required on site to identify the public IP address of a remote router. Installations can be reviewed remotely to see whether the installation was sufficient with regards to the signal strength received to obtain certain transfer speeds.
Provided the Internet connectivity source is unrestricted, these routers can be remotely accessed and port forwarding rules can be implemented in order to cater for remote access of networked devices. This ability mitigates the need to send technicians to remote sites to survey problems as many of the ‘smaller’ issues could be resolved through remote diagnosis.
Less complex applications which are also supported by these industrial routers include the wireless Ethernet bridge WLAN mode as well a standard VPN client connection. The wireless Ethernet bridge lends itself to environments where there may be an existing Wi-Fi network with Internet connectivity, to which the router connects and provides that Internet access to its LAN devices. The VPN connection support suits applications which may link multiple sites such as linking satellite offices to the head office’s main server.
These feature-rich WLINK routers are a perfect fit for many applications including remote data monitors, CCTV surveillance systems, remote POS/ ATM, vending machines, telemetry, vehicle surveillance and control, and bus hotspots.
For more information contact Otto Wireless Solutions, +27 (0)11 791 1033, stephen@otto.co.za, www.otto.co.za
| Tel: | +27 12 803 7373 |
| Email: | dominic@ottomarketing.co.za |
| www: | www.ottomarketing.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Otto Online |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved