
By democratising wireless communications through space, internet providers aim to provide access to 50% of the Earth’s population currently disconnected from terrestrial networks (TN). The incorporation of
non-terrestrial networks (NTN) in the latest 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Rel-17 poses significant technical and business challenges. This integration mandate pressures the communications industry to transform the envisioned goal into a tangible reality.
Besides offering connectivity to subscribers in the current unserved and underserved locales, and enabling applications such as the Internet of Things, this not-so-futuristic vision of wireless connectivity plans to leverage airborne stations and high-altitude platforms (HAPs) such as uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), balloons, or dirigibles, shown in Figure 1. Developers intend to use this infrastructure to complement existing terrestrial networks and enable seamless connectivity worldwide.
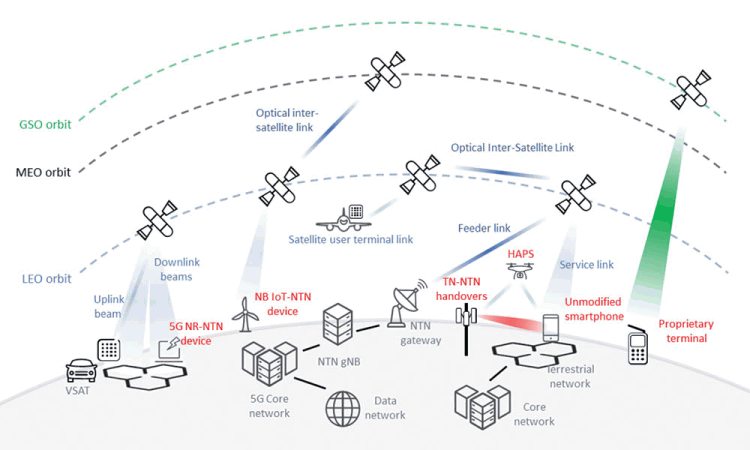
5G NTNs leverage many features from 5G terrestrial networks because they face similar challenges. Because of this, there are heightened reliability expectations for 5G NTN services compared to earlier SATCOM networks. Handheld or vehicle-based user equipment (UE) demands high volumes of data for video and mapping services. Alternatively, sensor applications connect multiple user equipment, with lower data rates.
Delivering the required volumes of data means leveraging 5G signalling fundamentals for 5G NTN. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has already designated 5G spectrum exclusively for terrestrial networks. The deployment of tens of thousands of satellites for 5G NTNs introduces even more spectrum crowding.
Integrating terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks
The primary focus of an NTN is to offer coverage in underserved areas. An essential aspect that sets 5G NTN apart from previous technologies is its seamless integration with existing terrestrial network infrastructure. This integration unlocks the following new opportunities and use cases:
• Public safety for critical communications provides a backup in the absence of cellular coverage due to terrestrial network shutdowns, natural disasters, and emergencies.
• 3D coverage supports reliable communications when using aerial moving objects like balloons or UAVs, increasing the provision of multidimensional coverage and seamless transition.
• Massive IoT enables global coverage, alleviates cross-country border challenges, and optimises power consumption and network resources when moving between TN and NTN as needed.
To read the full white paper visit www.dataweek.co.za/*ad5gntn
| Tel: | +27 12 678 9200 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.concilium.co.za/test-measurement |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Concilium Technologies |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved