
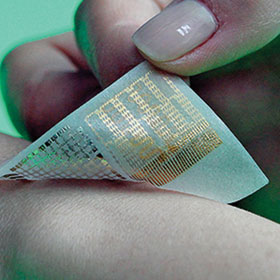
The requirements for an elastic plaster, or band-aid, are few and trivial by 21st century standards: it needs a soft absorbent section, a sticky section that’s sticky enough to adhere to skin, and should ideally be waterproof.
But what if it could also measure things like muscle tremors? And store a person’s medical data? And release drug-containing nanoparticles? Charlie Sheen need not lift a finger to get a fix ever again.
That’s probably not the application that researchers from Korea and the USA had in mind when they began collaborating on new technology that offers a glimpse into the future of wearable medical devices: they have made a skin patch that’s thinner than a sheet of paper and can detect subtle tremors, release drugs on demand, and record all of this activity for subsequent review.
While an actual, sellable product is still some ways off, the research team did demonstrate a proof of concept that released a dye onto a patch of pig skin. In the words of the project’s leader – Dae-Hyeong Kim, assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering at Seoul National University – “the system represents a new direction in personalised health care that will eventually enable advanced diagnostics and therapy on devices that can be worn like a child’s temporary tattoo.” The plaster takes advantage of developments in stretchable electronics achieved by MC10, a startup in Massachusetts.
Under the skin of the high-tech plaster are spring-like strain gauges that measure muscle activity via silicon nanomembrane sensors in a serpentine shape, each curve several hundred micrometres apart. When stretched, changes in electrical resistance on the filaments are detected, and the frequency of the signals indicates whether a stretch was from a normal arm movement or a fast tremor.
The patch also contains heating elements that can be activated remotely to release drugs. These raise the patch’s temperature several degrees, which in turn releases drugs surrounded by porous silica nanoparticles. When heated, the physical bond between the drug and nanoparticles breaks, leading to a diffusion-driven release of molecules through the skin.
Data is recorded on a simple memory system consisting of memory cells just 30 nanometres thick; these cells record high-resistance versus low-resistance states due to changing electrical properties across the membranes. In the future, the researchers say these data could be accessed through an RFID tag integrated into the device, or might be streamed to a nearby smartphone; however, the communications component has not yet been added.
While the prototype is focused on detecting movement disorders, other versions could sense things like perspiration, temperature, heart rate or blood oxygen, and use those changes as a triggering mechanism for various therapies. The teams are working to bring this platform through regulatory and clinical studies.
Unfortunately, given the fact that electronics and water don’t get along particularly well, hopes that this high-tech plaster could be made waterproof may be a bit of a ‘stretch’.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved