
Antenna polarisation may be one of the least understood properties of a wireless signal. If you are installing many antennas in one location, like on a tower, polarisation is an important piece of the puzzle that you'll need to take into consideration.
Polarisation is determined by the way an antenna is mounted, usually horizontally or vertically. To ensure optimal network performance only like-polarised antennas should be used in point-to-point wireless applications. It is possible to establish a wireless link using antennas with different polarities but network performance and connectivity will suffer.
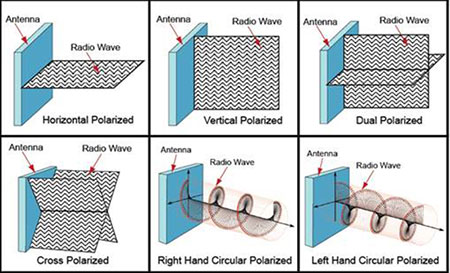
The big advantage of using different antenna polarisation schemes is to reduce interference. For example, when mounting several antennas on a tower, it is best to stagger vertically and horizontally polarised antennas to reduce interference. If horizontal or vertical polarisation won't work for your wireless application there are dual-polarised, cross-polarised and circular-polarised antenna options to explore.
Dual-polarised antennas feature two antenna elements in a single physical package (radome), one that is vertically polarised and one that is horizontally polarised. When properly installed, dual polarised antennas can communicate with both vertically and horizontally polarised antennas. An advantage of dual polarity antennas is that you get basically two antennas in one package, saving space and money. These types of antennas are often used with MIMO (multiple-in/multiple-out) wireless access points and CPE (customer premises equipment) devices.
Cross-polarised antennas, sometimes referred to as X-Pol antennas, feature two elements in one package. One element is +45° polarised and the other is -45° polarised. The two opposing 45° angles of the elements produces a cross or X orientation. Using a cross polarised antenna with vertically and horizontally polarised antennas further reduces interference.
Circular-polarised antennas have equal response to either horizontal or vertical polarised antennas. These antennas are designed to either support right-hand or left-hand polarisation to suit varied wireless connectivity applications. Using a circular-polarised antenna on a fixed access point can be beneficial if the linear-polarised remote links are constantly moving.
For more information contact Andrew Hutton, RF Design, +27 21 555 8400, [email protected], www.rfdesign.co.za
| Tel: | +27 21 555 8400 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.rfdesign.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about RF Design |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved