
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the culmination of progression that has been made within a number of different, interrelated technology disciplines in recent years.
Through major advances in wireless connectivity and sensing, as well as support given by processing, control and power management devices, the stage is now set for IoT to start seeing widespread deployment in both consumer and industrial spheres.
The purpose of the following white paper is to look specifically at Industrial IoT (IIoT). It will describe the commercial dynamics and market trends that are defining this particular sector. In addition, it will give details of the various design issues being faced by engineers as they look to develop and implement IIoT systems, then explain how these challenges may be overcome.
Looking at the Industrial IoT (IIoT) market specifically, industry analyst firm, Market & Markets, estimates that by 2022 the global IIoT business will be worth around $195 billion annually. There are many factors that will drive this growth, but the principle ones are for companies to be able to:
• Gain from more efficient working practices, through access to and subsequent analysis of the large quantities of data derived.
• Respond quicker to incidents that might occur which could otherwise have costly or dangerous outcomes, such as a fault arising or some deviation in an industrial process.
• Be notified more quickly for places where maintenance (or other pre-emptive measures) might be required to prevent faults that could impact operations in the long term.
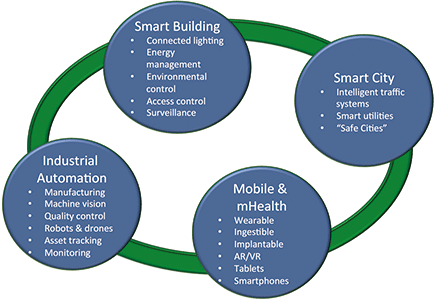
IIoT can enable higher degrees of automation and thus raise productivity. It can also help companies to broaden the array of services they can offer, heighten safety, avoid downtime (and the financial expense associated with this), better control their assets and also become more ecologically responsible. The fundamental technologies that will form the basis of IIoT implementations are connectivity, sensors and actuators.
Connectivity
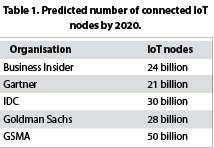
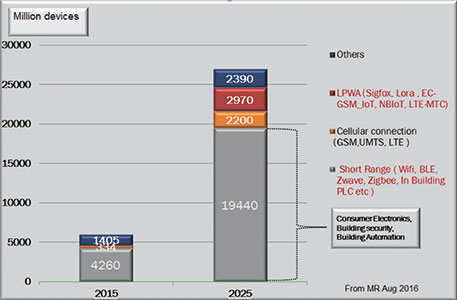
Predictions about the number of connected IoT nodes that will be in operation vary quite considerably. Table 1 gives a detailed summary of the forecasts being made by different organisations. The most ambitious suggest there will be 50 billion by 2020, while others claim 20 to 30 billion is a more realistic figure by that stage (though they expect the 50 billion mark to still be reached or even surpassed, just further into the next decade). What is certain is that there will be tens of billions of objects being connected to the Internet over the course of the next few years, and around 50% of these will be for some type of industrial application.
There are a multitude of different connectivity technologies offered that will support IIoT. Some of these are already established, while others are still in the process of emerging. They include traditional industrial wireline protocols (such as CAN bus, FieldBus, Hart, KNX, Ethernet, MBUS and PLC), as well as wireless protocols.
The wireless connectivity options can be categorised as either cellular-based ones that cover the wide area network (like LTE-M, and in the future, 5G) or short-range, power-efficient ones (like Wi-Fi, LoRa, ZigBee, Z-Wave and BLE) for ‘last mile’ implementation.
Actuators
IIoT presents an opportunity to control different mechanisms remotely via cloud-based automation infrastructures, including activating lighting, driving motors, opening/closing actions, etc.
The advent of smart lighting and smart motor control will have real tangible benefits to society, in terms of greater convenience and marked energy savings. Li-Fi communication technology, for example, is now permitting the ability to interface with what were previously conventional standalone actuators.
Sensors
Likewise, the capture of data through instrumentation will be pivotal to making system deployments effective.
Different sensor technologies can be employed in an IIoT context, providing valuable insight – on the temperature at which an industrial process is being conducted (to ensure that it is running correctly), the ambient light and moisture levels in a large commercial greenhouse (to check that conditions are correct to allow maximum crop yield), or nitrogen-oxide content in gas leaving the exhaust flue of an industrial boiler.
Outside the industrial engineering sector, other types of sensors can be utilised for different tasks that are still categorised under the IIoT umbrella. In building automation, passive infrared devices can be used to provide motion detection, for controlling the lighting/heating or alternatively for security purposes. In healthcare, sensor technologies will allow remote monitoring of parameters, such as blood glucose levels. This will result in significant improvements in the quality of patients’ lives, as they will be able to spend less time in hospitals/clinics.
For sensor-connected networks, the power consumption of the object is likely to be significantly less than will be the case for connected actuators, hence battery-powered objects will represent the vast majority of deployments. This is likely to prove critical to IIoT proliferation, as many applications will rely on sensors that have been deployed in remote locations (and therefore sending engineers out into the field to regularly replace batteries will be uneconomical).
The power consumption and connection range of the radio interface will potentially represent a significant impact on the lifespan of the battery, so BLE and other ultra-low power RF protocols will be preferable. In some cases energy harvesting will be employed to take care of the power supply problem, enabling batteries to simply be dispensed with.
Practicalities of IIoT deployment
In addition to the limitations placed on IIoT hardware due to battery-powered operation, the electronics located at each node are likely to have other constraints. The large number of nodes deployed could mean that low bill-of-materials costs need to be adhered to. Furthermore, available space may also be restricted.
These factors mean that often IIoT objects will generally have only limited microprocessor and memory resources that they can draw upon. Consequently, their construction must be as sleek as possible, with no excess functionality incorporated.
Cloud services and supporting infrastructure
The cloud will be the foundation upon which IIoT data processing and storage activities are reliant. In the realm of consumer IoT, the data that is captured and transported to the cloud may be required for marketing analysis (for example), without any subsequent involvement from the user.
In contrast to this, however, IIoT-based data (concerning industrial processes, confidential medical records, etc.), must be managed under extremely strict control procedures and with authorisation of the owner of this data. To mitigate the potential threat of industrial espionage, hacking or even acts of terrorism, a fully secured service offering needs to be employed - this can either be software as a service (SaaS) or platform as a service (PaaS) based.
The revenue that IoT/IIoT services will constitute is far bigger than both hardware and connectivity elements combined, and is also growing at a much faster rate (this is illustrated in Figure 3). As we will see, the hardware and cloud service providers looking to serve the IIoT market are only focusing on their own established area of expertise.
![Figure 3. Comparison of projected revenues relating to services with rest of IoT ecosystem [source: ABI Research].](articles/Dataweek - Published by Technews/k5221e.jpg)
This is having a detrimental effect on the uptake of IIoT technology though, as the hardware and software development aspects have to be addressed separately. The ‘silo’ approach that is currently prevalent has to be altered considerably. What the industry needs instead is an all-encompassing solution that deals with both these key elements together – so that hardware engineers have the warranted support, but at the same time software developers are able to create the cloud-based apps that will accompany that hardware.
Another consideration is the versatility of the hardware itself. Currently, semiconductor vendors supply generic single-board development solutions with a certain set of sensor and connectivity functions built in. This leaves little scope for engineers to optimise the system in accordance with their particular application criteria though.
Far more appealing would be a flexible platform, where they could choose from a broader array of different sensor, actuator and connectivity options, just adding the ones that they actually required.
An IoT development kit
ON Semiconductor recognised early on that something needed to be done about the disjointed situation that exists between the hardware and software aspects of IoT/IIoT development. Its technical staff were given the job of attempting to bridge this gap – bringing a solution to market that covered both distinctive types of competency.
The objective was to provide hardware engineers (who had little knowledge of cloud-based software development) with an out-of-the-box solution via which they could access cloud-based services, while at the same time giving more experienced embedded software experts provision to change to another cloud service provider or to develop their own proprietary services from the ground up.
The result of this endeavour was the ON Semiconductor IoT Development Kit (IDK). This presents engineers with a ready-to-use single platform that exhibits a high degree of flexibility, upon which the demands of both hardware and software are fully accommodated.
Based on the company’s highly sophisticated NCS36510 system-on-chip (SoC) with a 32-bit ARM Cortex M3 processor core, it has all the necessary hardware resources for constructing highly effective, differentiated IIoT systems, along with a comprehensive software framework to attend to interfacing with the cloud.
By attaching different daughter cards to the IDK baseboard, a wealth of connectivity (Wi-Fi, SIGFOX, Ethernet, 802.15.4 MAC-based radios enabling ZigBee and Thread protocols, etc.), sensor (motion, ambient light, proximity, heart rate, etc.) and actuator (with stepper and brushless motor driving, plus the ability to drive LED strings) options can be added to the system. This means that compromises do not have to be made and the most suitable technology can be chosen.
The Eclipse-based integrated development environment (IDE) that accompanies this hardware consists of a C++ compiler, debugger, code editor and a collection of application-related libraries. Through the use of the Carriots PaaS, it is possible to give engineers the functionality needed to interface with the cloud, but without putting any major restrictions on the scope of their creativity. It allows them to configure the IDK in the way that best fits with their particular application, but simultaneously still benefiting from powerful security features and real-time diagnostics/analytics.
The IDK provides a highly configurable platform that will help engineers to achieve their system design goals while accelerating development timeframes – thereby getting systems deployed much quicker and with greater cost effectiveness.
For more information contact Dirk Venter, Altron Arrow, +27 11 923 9600, [email protected], www.arrow.altech.co.za
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved