
Linear Technology's LT1684 was specifically designed for OEM telephone equipment. Its function is to interface between the digital control logic and the high voltage analog phone line. When used in the design of a phone system, the LT1684 allows software to control the frequency , voltage and cadence of the ring signal.Because of similarities of application to telephone systems, the LT1684 ring tone chip finds itself at home in motor drives, digital input amplified speakers, alarm systems and sine wave UPS systems.
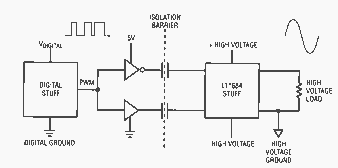
The LT1684 provides the tool set to easily implement a digital, pulse width modulated (PWM) signal to DC-coupled voltage converter (at high currents), while providing isolation, switching frequency filtering and output protection. Figure 1 is a system-level diagram of the LT1684 in action. By controlling a pair of external MOSFETs, the LT1684 provides up to ±240 V of smooth, clean output at up to 200 mA of output current. Higher output voltages are obtained by cascoding MOSFETs, while higher currents are readily achieved by using the LT1166 MOSFET automatic bias generator chip as a com-panion.
The circuit
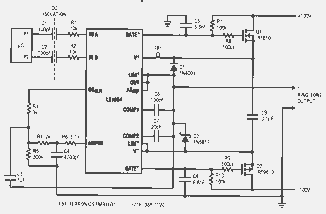
Figure 2 shows its use in a digital PWM-to-ringing telephone converter. This is something like a high power, high voltage, isolated, output filtered D/A converter. Like its DAC counterpart, the LT1684 has a precision reference, switches and an output amplifier. Unlike its DAC counterpart, it includes post-conversion ripple filtering, isolation and a robust high voltage output.
In addition to the isolation, filtering and amplification, the LT1684 provides the gate-bias control and gate voltage protection for the two external MOSFETs. Providing such a plethora of functions from a single, monolithic IC requires the use of a somewhat tricky circuit. This circuit is arrived at by applying a circuit transformation to a simple filter circuit. See the basic 2nd order lowpass multiple feedback filter (MFB) circuit which looks somewhat like the filter/amplifier in Figure 3. The filter/amplifier components in Figure 2 are R3-R5 and C3 and C4. Looking backwards through the circuit transformation, these components, in fact, form the 2nd order MFB filter shown in Figure 3. The values chosen for these components in Figure 2 implement a 2nd order Butterworth MFB lowpass filter with a cutoff frequency of 100 Hz and a DC gain of 100. These were chosen to provide ±80 V of output swing with PWM duty factors of 10 to 90%, while filtering the 10 kHz PWM ripple to meet telephone specifications.
Stealing the LT1684 for use in other applications
The LT1684, used as shown in Figure 1, outputs a ring signal that meets Belcore specification. This means it can ring a phone 22 000 feet away. The LT1684 fits another role, where 22 000 feet of separation would be a nice minimum. This is the application of the LT1684 in the scalable power amplifier, as detailed in Figure 4. This amplifier can be used to drive motors, simulate the power company in sinewave UPS systems and operate large audio drivers. Because of its scalable nature, this design can be used at any power level. The circuit in Figure 4 is shown implementing a 5000 W bits-to-decibels converter.
When this converter is implemented with the appropriate audio drivers and enclosures, the output sound pressure level can be significant - so significant, in fact, that this author suggests giving it a wide berth of at least 22 000 feet.
Analog inputs welcome
The scalable amplification system detailed in Figure 4 can be driven with analog inputs while still maintaining full isolation. Such a system is detailed in Figure 5, where the analog input is filtered (to prevent aliasing) and converted to PWM. Figure 5 goes on to show the use of an RS485 differential driver to drive a twisted pair line. The receiver end of the twisted pair line is terminated with a resistor and put across the isolation barrier. This provides very good ESD protection on both ends of the line.
Conclusion
The LT1684 is useful in a wide variety of applications. It is a highly integrated solution for use in any system that requires digital control of high output voltage or high output power.
For further information contact Linear Technology's South African representative Multitech Electronics Corporation, (021) 674 4103.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved