
Facing dwindling profits, fewer opportunities to expand by taking market share from competitors, and a shrinking roster of star performers, the semiconductor industry has entered a period of lowered expectations and diminishing options, forcing chip suppliers to rethink their basic strategies for success, according to iSuppli.
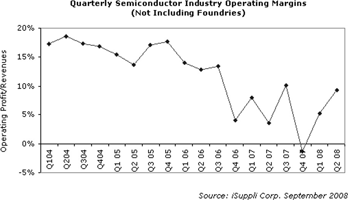
“Semiconductor profitability has eroded steadily since mid 2004, with quarterly net profits having fallen into the single-digit range in 2008, down from the 17% to 19% range in 2004,” said Derek Lidow, president and chief executive officer of iSuppli. “The semiconductor industry now is less profitable as a percentage of revenue than the notoriously low-margin PC business, something that has not occurred before, except during a short period of the severe market downturn in 2001.”
“To a degree, conditions in the semiconductor industry have been impacted by short-term events, such as the market volatility in 2006 due to inventory write-offs and price wars in major product segments like DRAMs and microprocessors,” Lidow observed. “However, the long-term trend indicates that the semiconductor industry – which historically has been good at capturing profits in the electronics value chain – seems to have lost its money-making touch.”
Haves and have-nots
As profit has diminished, the semiconductor industry has re-segmented itself into new groups, according to Lidow.
During the period of 2001 to 2004, semiconductor companies seemed to fall into three categories: a small group of firms whose growth outperformed the market; a middle-performing group consisting of most suppliers and a set of low performers at the bottom. The top caste of suppliers typically employed predatory business strategies that enabled them to take market share from weaker competitors.
The lowest performers often served as the market-share prey for the predators and the middle-range of suppliers. However, during the just completed semiconductor business cycle from 2004 to 2007, the prey in the lowest caste of suppliers went extinct – and so did the success of predatory strategies, creating a larger group of middle-performing players.
“The number of low performing companies decreased by so much that there are now only two major distributions in the industry: a few outstanding performers and the rest,” Lidow said. “The number of competitors achieving growth of more than 100% during the period of 2004 to 2007 declined to nine, down from 19 during the period of 2001 to 2004. This shows semiconductor companies can no longer break out of the pack by taking market share away from weaker rivals.”
Breaking away
So how can semiconductor companies be expected to break out of the current market dynamics to outperform the industry?
One proven strategy for success for semiconductor suppliers is to go out and capture value from their customers by designing more of the total system with system-level chips built around proprietary Intellectual Property (IP). Companies that pursue such strategies are consistently more profitable and faster growing than their peers. Examples include Qualcomm, MediaTek and Linear Technology.
Another strategy is to milk established cash-cow products in the industry. Such cash-cow products are typically trailing-edge devices that have passed through their commodity stage, have fairly steady pricing and have a dwindling number of suppliers that are willing to devote their best people to designing and managing products that most semiconductor cowboys would find boring. Sellers of such devices include Microchip, Diodes, Microsemi and Rohm.
Finally, well-heeled semiconductor suppliers can use their resources to massively outspend their rivals in the areas of products and manufacturing, and thus maintain technical and scale dominances in competitive market segments. Companies employing such strategies include Samsung Electronics, Intel and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC).
The wages of mediocrity
As semiconductor companies attempt to pursue such strategies, they will have to face the reality that the electronics industry has become increasingly unforgiving of mediocrity in any area because such underperformance drains profits as well as device and operational performance. Furthermore, semiconductor buyers expect their suppliers to be first rate in all pursuits, ranging from process technology to marketing, a standard that many companies can meet.
“In this day and age, semiconductor suppliers have the opportunity to outsource any or all of their operations to third party sources that offer world-class work,” Lidow observed. “Those semiconductor companies that are unable to achieve top quality and performance in all processes, either through outsourcing or by using internal resources, will be punished in the marketplace.”
For more information visit www.isuppli.com

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved