Graphene's electronic behaviour probed
10 November 2010
News
Using a one-of-a-kind instrument designed and built at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the US, an international team of researchers has unveiled a quartet of graphene’s electron states and discovered that electrons in graphene can split up into an unexpected and tantalising set of energy levels when exposed to extremely low temperatures and extremely high magnetic fields.
Published in the 9 September 2010 issue of Nature, this new research raises several intriguing questions about the fundamental physics of this exciting material and reveals new effects that may make graphene even more powerful than previously expected for practical electronic applications.
Graphene is one of the simplest materials – a single-atom-thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like lattice – yet it has many remarkable and surprisingly complex properties. Measuring and understanding how electrons carry current through the sheet is important to realising its technological promise in wide-ranging applications, including high-speed electronics and sensors. For example, the electrons in graphene act as if they have no mass and are almost 100 times more mobile than in silicon. Moreover, the speed with which electrons move through graphene is not related to their energy, unlike materials such as silicon where more voltage must be applied to increase their speed, which creates heat that is detrimental to most applications.
NIST recently constructed the world’s most powerful and stable scanning probe microscope, with an unprecedented combination of low temperature (as low as 10 millikelvin, or 10 thousandths of a degree above absolute zero), ultra-high vacuum and high magnetic field. In the first measurements made with this instrument, the team has used its power to resolve the finest differences in the electron energies in graphene, atom by atom.
Because of the geometry and electromagnetic properties of graphene’s structure, an electron in any given energy level populates four possible sublevels, called a ‘quartet.’ Theorists have predicted that this quartet of levels would split into different energies when immersed in a magnetic field, but until recently there had not been an instrument sensitive enough to resolve these differences. The experiment, according to the research team, revealed unexpected complex quantum behaviour of the electrons in a high magnetic field at extremely low temperatures. The electrons apparently interact strongly with one another in ways that affect their energy levels.
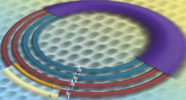
This artist’s rendition illustrates the electron energy levels in graphene as revealed by a unique NIST instrument. Because of graphene’s properties, an electron in any given energy level (the wide, purple band) comprises four quantum states (the four rings), called a ‘quartet.’ This quartet of levels split into different energies when immersed in a magnetic field. The two smaller bands on the outermost ring represent the further splitting of a graphene electronic state
One possible explanation for this behaviour, the team says, is that the electrons have formed a ‘condensate’ in which they cease moving independently of one another and act as a single coordinated unit. If so, the work could point the way to the creation of smaller, highly energy efficient electronic devices based upon graphene which produce very little heat.
Further reading:
Electronic News Digest
News
A brief synopsis of current global news relating to the electronic engineering fields with regards to company finances, general company news, and engineering technologies.
Read more...
4000 A containerised DB for power project
News
Power Process Systems has successfully completed the design, fabrication, and commissioning of a 4000 A containerised distribution board for a wind/PV solar hybrid renewable energy project.
Read more...
Datacentrix Industrial Indaba 2025
News
Datacentrix recently hosted its inaugural Industrial Indaba 2025, where industry leaders explored how digitalisation, resilience, security and compliance are shaping the future of sustainable industrial operations in Africa.
Read more...
RS brings solar light to 150 000 people
RS South Africa
News
The company’s three-year partnership with SolarAid aims to raise £1 million through corporate donations, matched funding, product contributions, and fundraising to accelerate access to safe, sustainable energy.
Read more...
Microchip and AVIVA Links collaboration
Altron Arrow
News
Microchip and AVIVA Links have achieved groundbreaking ASA-ML interoperability, accelerating the shift to open standards for automotive connectivity.
Read more...
World’s leading supplier of grid automation products
News
Hitachi Energy was recognised as the global market share leader in grid automation for electric power transmission and distribution utilities by ARC Advisory Group.
Read more...
Vivashan Muthan appointed as head of export sales and operations at RS South Africa
RS South Africa
News
With a career spanning engineering, business development, and sales leadership across sub-Saharan Africa, Vivashan Muthan brings a wealth of expertise to his new role as head of export sales and operations.
Read more...
Google equips university students across Africa with free access to advanced AI tools
News
A 12-month Google AI Pro plan has been launched for students in Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa, and Zimbabwe to build foundational AI skills.
Read more...
Africa’s space economy projected to be worth $22,6 billion in 2026
News
South Africa is gearing up to be at the forefront of the growth in the space industry, creating thousands of jobs, driving innovation, and boosting the national economy.
Read more...
Distribution partnership with MacDermid Alpha
Testerion
News
MacDermid Alpha Electronics Solutions India Private Limited has announced that as of 01 September 2025 Testerion will be the sole importer and distributor of their products to the South African market.
Read more...


