Transceiver architectures for low-cost radios - Part I
9 April 2003
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Access Control & Identity Management
Steve Moore, director applications, Micro Linear
Anyone who has ever worked in the wireless field knows there are as many different wireless implementations as there are useful applications. Many of today's systems engineers continue to have difficulty specifying detailed radio requirements and evaluating possible trade-offs in performance. At times it seems easier to just select one of the popular wireless systems that we hear about everyday (eg, 802.11, Bluetooth) and not sweat the specifics of the wireless implementation.
For applications where interoperability is a requirement this is a logical (and necessary) choice, but for many other wireless applications (eg, cordless phones, industrial control, consumer game controllers, meter reading, wireless audio, security) systems designers can usually reduce size, cost, and power by using highly-integrated RF transceivers (like the Micro Linear ML2724) and developing simple radio protocols optimised to the specific application.
For example, using an 802.11 solution running at 11 Mbps with carrier sense multiple access, full TCP/IP stack, encryption, and PCMCIA host interface for anything other than a high-speed, Ethernet-compatible wireless network will almost certainly result in unnecessary cost, size, and power. Likewise, a Bluetooth solution, while much lower cost and lower power than 802.11, still carries the additional overhead associated with a complex peer-to-peer personal area network (PAN) designed with interoperability as its primary feature.
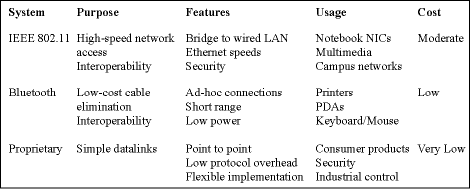
The downside of adopting standards-based solutions is that in a lot of wireless applications these solutions have many features not required resulting in unnecessary cost and power. Table 1 shows a simple comparison of the features, intended purpose, and relative cost between some of the more popular solutions.
To effectively realise an optimal wireless solution doesn't have to be complex and mysterious, especially with today's highly integrated radio transceiver ICs. Knowing basic radio specifications and how to choose a radio architecture and link protocol is all that is necessary.
Table 1. Comparison of common wireless systems
In a subsequent issue of Dataweek I will present Part II of this series that will describe some of the basic system-level radio specifications to consider along with a brief overview of common radio architectures found in today's integrated transceivers.
For more information contact Kevin Jurrius, Components & System Design, 011 979 4274.
Further reading:
Mobile satellite connectivity available in SA
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Space42 has commercially launched its next generation mobile satellite service, Thuraya 4 NGS, available in South Africa as of February 2026.
Read more...
Next-gen Wi Fi 6E connectivity for embedded systems
iCorp Technologies
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Espressif Systems has expanded its connectivity portfolio with the introduction of the ESP32-E22, the company’s first Wi-Fi 6E connectivity co-processor.
Read more...
Quectel redefines connectivity with RG660Qx 5G Series
iCorp Technologies
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Purpose-built to meet the demands of next-generation IoT and wireless broadband, these modules leverage the cutting-edge Qualcomm X85 and X82 5G Modem-RF systems to deliver enterprise-grade performance.
Read more...
Centurion raises the bar at HomeSec Expo
Centurion Systems
News & Events Access Control & Identity Management Residential Estate (Industry) Smart Home Automation Commercial (Industry)
Centurion Systems unveiled its latest product lines at HomeSec Expo 2026, introducing SMART+, a simpler way for installers and end users to manage their Centurion installations - as well as a few new products.
Read more...
Contactless IO-Link couplers
IOT Electronics
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The IO-Link couplers from Phoenix Contact are industrial contactless couplers designed to transmit power and IO-Link data across a small air gap without physical connectors.
Read more...
Quectel’s RG255C-NA and RM255C-GL accelerate 5G RedCap adoption
iCorp Technologies
Editor's Choice Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Quectel’s RG255C-NA and RM255C-GL modules represent a strategic move into this fast-growing segment, delivering Sub-6 GHz 5G connectivity optimised for mid-tier IoT applications.
Read more...
SDRs – Which RF architecture should you choose?
RFiber Solutions
Editor's Choice Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
There are several common methods of implementing SDR architectures. This paper discusses which is best when meeting a specific need.
Read more...
Multi-band GNSS patch antenna
RF Design
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The Taoglas AHP2356A is a compact, high-performance active GNSS patch antenna designed for next-generation positioning systems requiring precision, reliability, and multi-constellation support.
Read more...
Cellular routers for explosive areas
Phoenix Contact
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Updated versions of the Cellulink outdoor cellular router product range from Phoenix Contact are now available; they have been specially developed for use in Zone 2 potentially explosive areas.
Read more...
Power the next wave of IoT innovation
Links Field Networks
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Links Field Networks’ portfolio includes connectivity platforms, edge devices, and network management tools designed to support secure, resilient IoT deployments across a range of use cases.
Read more...