The development of a reverse-blocking IGBT for use in matrix converters
10 August 2005
Power Electronics / Power Management
Information from Mitsubishi Electric
Currently, the method most often used to control the frequency of three-phase AC power in equipment for power applications uses inverters. The matrix converter method is currently the focus of attention as an alternative that will eventually replace this inverter method.
Because the switches from which matrix converters are built require reverse-blocking IGBTs which, as their name suggests, can block current in the reverse direction, power devices used for matrix converters have, in the past, been made from IGBTs in series with diodes.
Mitsubishi Electric has developed a reverse-blocking IGBT as a power device for use in matrix converters. As shown in the Figure, the reverse-blocking IGBT surrounds the IGBT cell region by a deep diffusion-isolation P-layer that extends all the way to the back surface, so that the interface between the N-layer and the P-type collector layer on the back surface is not exposed on the dicing surface. As a result, this structure can block a reverse current because the depletion layer extends from the diffusion-isolation P-layer and the P-layer on the back surface to the N-layer when a voltage is applied in the reverse direction.
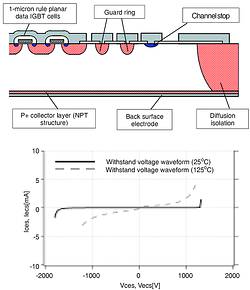
The current/voltage waveform when a reverse bias is applied to the prototype reverse-blocking IGBT developed in the project is also shown. The horizontal axis shows the collector-emitter voltage (VCES) when the gate is shorted to the emitter, and the vertical axis shows the collector cut-off current (ICES). At 25°C, the reverse-blocking IGBT could block voltages of over 1300 V in the forward direction and over 1500 V in the reverse direction. Even at 125°C, the prototype had a blocking capability of 1200 V, although there was some increase in the leakage current.
The resulting reverse-blocking IGBT has succeeded in matching the performance of third-generation planar IGBTs in terms of the trade-offs between saturation voltage and switching loss, the key characteristics of an IGBT, while still maintaining the withstand voltage in both forward and reverse directions. These characteristics are obtained through the use of fourth-generation planar MOS structure, along with a shallow P collector on the backside using Mitsubishi's proprietary thin-wafer technology. This reverse-blocking IGBT produces the effect of using a diode, and actual use has confirmed the absence of problems with the equivalent diode properties.
The performance achieved by this development gives substantial advantages over that of the conventional structure in which IGBTs are connected in series with diodes. It thus has an important role to play in developing the matrix converters of the future.
Further reading:
The importance of power integrity
Spectrum Concepts
Power Electronics / Power Management
[Sponsored] Behind every high-speed system lies the need for power integrity. Without it, even the cleanest signal paths become compromised.
Read more...
Precise multi-vital sign monitoring
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
The AS7058 by ams OSRAM is an integrated multi-vital sign monitoring device, which provides a complete photoplethysmogram, electrocardiogram, body impedance sensor, and electrodermal activity sensor.
Read more...
Automotive battery diagnostics tester
Comtest
Power Electronics / Power Management
Midtronics’ MVT handheld battery tester is a revolutionary tool, powered by MDX-AI, which is set to redefine the standards of battery diagnostics and testing in the automotive industry.
Read more...
Advanced 3-phase controllers
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
The STSPIN32G0 by STMicroelectronics is a family of highly integrated system-in-package providing solution suitable for driving three-phase brushless motors.
Read more...
Converting high voltages without a transformer
Altron Arrow
Editor's Choice Power Electronics / Power Management
With appropriate power converter ICs, such as the LTC7897 from Analog Devices, many applications can be suitably powered without having to use complex and cost-intensive transformers.
Read more...
Reliable power for demanding applications
Conical Technologies
Power Electronics / Power Management
The Mibbo Power MTR480 three-phase DIN-rail power supply is engineered to meet stringent industrial automation requirements, offering dependable performance in environments where downtime is not an option.
Read more...
Powering performance and precision
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
onsemi’s innovative T10 series MOSFETs, available in 40 V and 80 V versions, are designed for high-efficiency, fast-switching, and power-dense applications.
Read more...
Programmable flyback switcher ICs
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
Power Integrations has announced the release of the InnoSwitch5-Pro family of programmable flyback switcher ICs, which offer more than 95% efficiency in streamlined AC-DC converter designs.
Read more...
Multilayer chip beads with 8 A rating
RS South Africa
Power Electronics / Power Management
TDK Corporation has expanded its MPZ1608-PH series of large-current multilayer chip beads for automotive and commercial power supply lines.
Read more...
The role of bidirectional charging in the evolving energy landscape
Avnet Silica
Power Electronics / Power Management
As reliance on renewable sources like wind and solar continues to grow, the need for efficient energy flow and storage solutions has become more critical than ever.
Read more...


