
Mesh networking is a powerful way to route data. Range is extended by allowing data to hop node to node and reliability is increased by ‘self healing’, the ability to create alternate paths when one node fails or a connection is lost.
One popular mesh networking protocol is ZigBee, which is specifically designed for low-data rate, low-power applications. Digi International offers several products based on ZigBee. Additionally, the company has developed an alternate mesh protocol named DigiMesh. Both ZigBee and DigiMesh offer unique advantages important to different applications, as this article considers.
ZigBee nodes
The ZigBee protocol defines three types of nodes: coordinators, routers and end device, with a requirement of one coordinator per network - see Figure 1.
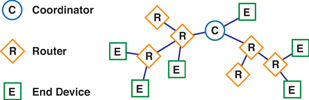
While all nodes can send and receive data, there are differences in the specific roles they play.
Coordinators are the most capable of the three node types. There is exactly one coordinator in each network and it is the device that establishes the network originally. It is able to store information about the network, including security keys.
Routers act as intermediate nodes, relaying data from other devices.
End devices can be low-power/battery-powered devices. They have sufficient functionality to talk to their parents (either the coordinator or a router) and cannot relay data from other devices. This reduced functionality allows for the potential to reduce their cost.
ZigBee offers these advantages:
* Open standard with interoperability between vendors.
* Option for lower cost, reduced function end nodes.
DigiMesh nodes
DigiMesh has only one node type. As an homogenous network, all nodes can route data and are interchangeable - see Figure 2. There are no parent-child relationships. All can be configured as low-power/battery powered devices.
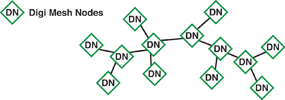
DigiMesh offers these advantages:
* Network setup is simpler.
* More flexibility to expand the network.
* Increased reliability in environments where routers may come and go due to interference or damage.
Sleeping routers
Allowing a node to sleep reduces power consumption, which is especially helpful for nodes that are battery powered. Currently, ZigBee allows for end devices to sleep but not routers or coordinators. DigiMesh allows all nodes to sleep, thereby increasing battery life.
Sleeping is allowed by time synchronisation. Some systems require a gateway or coordinator to establish time synchronisation. A significant advantage of DigiMesh is that it eliminates the single point of failure associated with relying on a coordinator or gateway. Instead, it establishes time synchronisation through a nomination and election process, enabling the network to operate autonomously.
Additional differences
Since ZigBee is an open standard, it offers the potential for interoperability with devices made by different vendors. This provides the ability to have over-the-air firmware updates. Furthermore, ZigBee offers established profiles for common applications such as energy management and lighting controls. A good selection of diagnostic support tools, like RF packet sniffers, is also available.
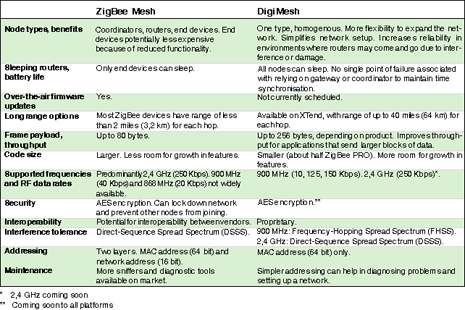
DigiMesh, as a proprietary protocol, allows for tighter control of code space and therefore more room for growth in features. It is available on platforms with longer range and more RF data rate options. Frame payload is generally larger, which can improve throughput for applications that send larger data blocks. Additionally, DigiMesh uses a simplified addressing method, which improves network setup and troubleshooting.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved