
Typical fleet management, security and tracking applications combine GPS positioning with GSM communication technology to provide actual position in real-time to a back office.
In the past, several suppliers have tried to integrate both GPS and GSM/GPRS into a single, hybrid component. Although technologically feasible, such a hybrid solution (module or chip) is from a commercial point of view destined to fail, due to the following reasons:
Combining both technologies into one hybrid component generally does not create a lower cost device. On the contrary, the extra packaging of both solutions adds cost; thus 1+1 does not add up to 2.
The two technologies, GPS positioning and GSM communication, run at a different development pace. It is almost impossible to combine the latest technologies for each into one hybrid component.
All components that use a communication technology such as GSM generally need to be certified and approved before being used in a country and on a network. Changing a hybrid GPS+GSM component to include the latest technologies for both would imply a new certification/approval procedure, each generating additional cost.
With its two technologies, for GPS and for wireless (GSM/GPRS and 3G), u-blox is following a different path: Instead of providing a hybrid component, u-blox increases the synergy between position and communication, between GPS and GSM, converging both technologies without integrating them. This leaves the customer with flexibility in design, choice of supplier, technology and price.
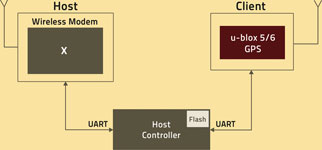
A block diagram of a typical system application for GPS and GSM is given in Figure 1: A host controller handles all communication with the GSM modem and with the GPS receiver, through separate I/O ports. The controller needs to be programmed for dealing with GPS and the GSM modem firmware.
With today’s advances in GPS positioning technology, one of the key elements is a fast GPS startup time, resulting in a fast position output. With AssistNow, u-blox has implemented a proprietary assisted GPS (A-GPS) solution, running on all u-blox GPS receivers of generation 5 and the soon-to-be-released generation 6. Traditionally, the firmware in the host controller (Figure 1) has to handle the AssistNow data and store it locally in non-volatile memory (Flash).
With its current GSM and upcoming 3G communication solutions, u-blox has implemented an AssistNow client in the modem, as indicated in the block diagram in Figure 2. The wireless modem handles all A-GPS data autonomously: it fetches the data from a (default or user-defined) server, stores the data in its own Flash memory and communicates with the GPS receiver whenever it requires the A-GPS for a fast startup; and without the wireless modem being in an active send/receive communication mode.
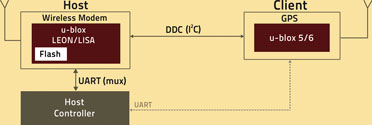
Naturally, the host controller still has to be able to communicate with the GPS receiver to obtain the position data. For this purpose, the wireless modem has a transparent path, through which the host controller can receive/send GPS messages, even without embedding them in AT commands. The direct connection between GPS and host controller can still be used.
This system configuration provides several advantages to designers. First of all, the synergies between the GPS and the wireless modem create a simpler and cheaper system solution. The firmware on the host controller does not have to be programmed in order to handle the A-GPS data; it is now just an AT command to the wireless modem telling it to start using AssistNow. Furthermore, flexibility in technologies is maintained: a customer can use a 5th generation (u-blox 5) based GPS receiver and replace it with tomorrow’s u-blox 6 GPS receiver. Alternatively, the LEON GSM/GPRS modem can, in the near future, be replaced with one of u-blox’ 3G modems.
With backward compatibility and embedded synergies, u-blox’ solutions provide added value and lower cost for system implementation.
| Tel: | +27 21 555 8400 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.rfdesign.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about RF Design |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved