
More reliable and efficient switched mode power supplies (SMPS) are continually in demand. Furthermore, SMPS designers are challenged to reduce products' size and weight. At the same time, the power consumption of applications increases constantly and there are an increasing number of legal requirements governing the efficiency ratings of power supplies. Infineon Technologies offers a range of SMPS semiconductors that enable the design of SMPS systems that fulfil existing and upcoming regulations and requirements for power factor correction (PFC) and standby power consumption.
Some SMPS topologies are shown below:
Boost converter
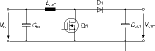
* Advantages: simple choke; no problems with magnetic coupling.
* Disadvantages: power transistor drain-source voltage VDS = V0 > V1; no galvanic isolation between input and output voltage; medium loading of the output capacitor.
* Parts: TDA 16888, TDA 4862, TDA 4863, CoolSET.
Flyback converter
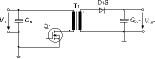
* Advantages: simple, low part count; several output voltages can be regulated simultaneously; wide control range for operating voltage changes.
* Disadvantages: power transistor drain-source voltage VDS = VIN + Nx (VOUT + VD1S); heavy loading to output capacitor and diode.
* Parts: TDA 16888, TDA 16846, TDA 16850, CoolSET.
Forward converter
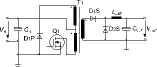
(single transistor forward converter/single-ended forward converter)
* Advantages: demagnetising the core no problem; simple circuitry.
* Disadvantages: power transistor drain-source voltage VDS > 2 V1: demagnetising winding is necessary; good magnetic coupling is necessary between primary and demagnetising windings.
* Parts: TDA 16888.
Two-transistor forward converter
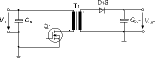
(diagonal half-bridge converter/dual-ended forward converter)
* Advantages: MOSFET drain-source voltage VDS = V1; core demagnetisation is no problem; the transformer may have a high level of stray inductance.
* Disadvantages: galvanic-isolated driving is necessary.
* Parts: TDA 16888.
Basic nonisolated sepic converter
* Advantages: transformer is replaced by two chokes; common ground connection; no polarity inversion low voltage stress for the MOSFET; output voltage is above or below the input voltage.
* Disadvantages: voltage at the diode is VIN + VOUT + VD1.
* Parts: TDA 16888, CoolSET.
Basic nonisolated Cuk converter
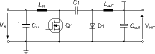
* Advantages: high efficiency; input/output current continuous; output voltage is inverse to input voltage.
* Disadvantages: high peak currents in power components; high ripple current in capacitor.
* Parts: TDA 16888, CoolSET.
Buck-boost converter
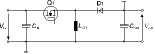
* Advantages: simple choke; no problems with magnetic coupling.
* Disadvantages: power transistor drain-source voltage VDS = V1 + V0; no galvanic isolation between input and output voltage; heavy loading of output capacitor; input must 'float'; output voltage negative in relation to input voltage.
* Parts: CoolSET.
| Tel: | +27 11 458 9000 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.electrocomp.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Electrocomp |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved