
For any industrial Internet of Things (IoT) application, ensuring signal integrity is crucial for safety and operational reliability. However, even the most robust system has many attack surfaces that are vulnerable to would-be hackers intent on compromising a system. This is unacceptable for high-reliability systems in general, but as more contextual information gets added, including time and position, the level of compromise increases dramatically, so gaps in security must be identified and closed at every opportunity.
In the case of an IoT sensor, a chain of trust must be established from the sensor to the microcontroller and wireless module, and all the way through to the end application. In industrial applications for the IoT, every attack surface must be secured in order to establish a chain of trust. u-blox refers to this as its five pillars of secure IoT design:
• Device firmware and Secure Boot.
• Communications to the server.
• Interface security.
• Enforcing API control.
• Robustness that includes handling spoofing/jamming.
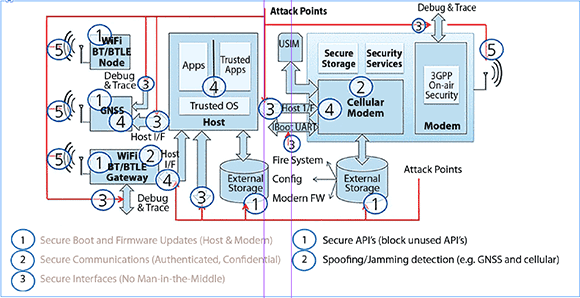
Secure Boot ensures that a device is executing the intended firmware by authenticating at each stage before booting the next process. Also, while over-the-air updates are useful for mass uploads of many widely deployed IoT devices, they create an attack surface that can be vulnerable, so all firmware must first be validated before being installed. A good implementation will include a backup of a previously authenticated image to allow backtracking if there is a problem.
At the communications or transport layer, a device needs to be able to authenticate itself with the server and all exchanged data should be encrypted, with no possibility of a ‘man in the middle’ attack. Secure key management will allow for this, even on a per-session basis.
The defined APIs that provide access to device functionality are also a vulnerability that must be addressed, though they are often overlooked. This is particularly insidious as hackers usually have a lot of time to look for open APIs and explore their relationship to device functionality and features, which sometimes might include access to paid services. Also, developers often use undocumented APIs for their own test and configuration purposes, so these must be protected too, using the same formal authentication and authorisation processes as used for all APIs.
The fifth link in securing IoT devices involves ensuring robustness, such as when facing jamming or spoofing attempts that might undermine the device’s ability to get accurate position data from a GNSS. The design must be able to detect that the reported information is not accurate and report the situation to the user or IoT network operator.
For more information contact Andrew Hutton, RF Design, +27 (0)21 555 8400, [email protected], www.rfdesign.co.za
| Tel: | +27 21 555 8400 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.rfdesign.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about RF Design |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved