Solution for synchronising multiple direct digital synthesizers
22 May 2002
DSP, Micros & Memory
The fast frequency hopping, extreme tuning resolution, and programmable phase control attributes of direct digital synthesizers (DDSs) make them a compelling choice for a wide variety of signal synthesis applications. However, many applications, such as phased-array radar and critical timing generators, require precise phase-synchronisation of multiple synthesized output signals. Phase synchronisation of multiple synthesizers is a challenge for PLL and other traditional analog-based architectures.
The AD9852/9854 and AD9850/9851 DDS devices from Analog Devices, with up to 14 bits of programmable phase-offset resolution (for AD9852/9854), provide an easy and precise solution for phase synchronisation of multiple synthesized signals. The synchronisation of multiple DDS devices is accomplished as follows.
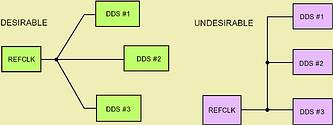
There are two basic timing requirements to be met in order for successful synchronisation to occur. The first, and somewhat obvious, is a coincidental REF clock between all DDSs. Coincidental means that the REF clock pins of each DDS have REF clock timing coincident in time (Figure 1). This is accomplished through proper PCB layout.
Figure 1. PCB layout must ensure that REFCLK edge arrives coincidentally at clock input pins of multiple DDSs
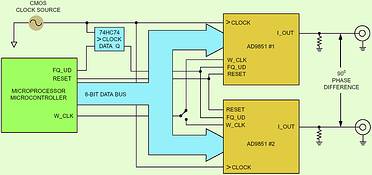
The second timing requirement between all DDS devices is the coincidental transfer of the programmed input data to the DDS core. Performing this transfer are two key signals: FQ_UD for the AD9850/9851 and I/O update clock for the AD9854/9852. If the rising edges of these two signals are sent synchronously to the multiple DDSs, along with proper set-up time relative to the REF clock, then synchronisation will be achieved (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Dual AD9851 set-up for quadrature output
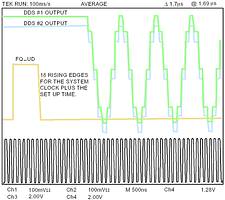
With proper procedure, synchronisation can be readily achieved among multiple DDSs; Figure 3 illustrates synchronisation of two AD9851 devices. In this case, the REFCLK frequency is set to 10 MSa/s. Synchronisation is also achievable up to the maximum system clock rate (including PLL mode).
Figure 3. DDS synchronisation (conditions: VCC = 5 V, REFCLK = 10 MSP, nonPLL mode, 25°C)
Typical applications are for clock synthesis, ADC encode generators, and agile local oscillators.
Further reading:
Quad RF ADC/DAC for wideband transceiver design
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
The AD9084 from Analog Devices integrates a quad 16-bit RF digital-to-analogue converter with a maximum sampling rate of 28 GSPS and a quad 12-bit RF analogue-to-digital converter.
Read more...
High-performance FPGA family
EBV Electrolink
DSP, Micros & Memory
AMD’s Kintex UltraScale+ FPGA family delivers high-performance, mid-range field programmable gate arrays that balance price, performance, and power efficiency for demanding DSP applications.
Read more...
Compact and scalable development board
DSP, Micros & Memory
The FRDM-MCXW72 from NXP is a compact and scalable development board for rapid prototyping of the MCX W72 multiprotocol wireless MCU.
Read more...
High-performance processing for cost-aware industrial IoT
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
STMicroelectronics has expanded its industrial processing portfolio with the new STM32MP2 series, a family of application microprocessors designed to deliver higher performance, advanced security and long-term reliability for cost-sensitive industrial IoT systems.
Read more...
Development board for secure industrial and IoT applications
DSP, Micros & Memory
The FRDM-i.MX93 Development Board from NXP is a compact, entry-level platform built around the powerful i.MX 93 applications processor, designed to accelerate prototyping and development for industrial, IoT, and edge computing applications.
Read more...
KIOXIA pioneer new 3D Flash technology
EBV Electrolink
DSP, Micros & Memory
KIOXIA Corporation and Sandisk Corporation pioneered a state-of-the-art 3D flash memory technology, setting the industry benchmark with a 4,8 Gb/s NAND interface speed, superior power efficiency, and heightened density.
Read more...
Ultra-wide signal capture from a single chip
RFiber Solutions
DSP, Micros & Memory
Jariet Technologies developed Electra, a chipset that enables ultra-wide, multi-function and multi-band signal capture and generation from a single component.
Read more...
High-performance processing at the edge
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
STMicroelectronics’ STM32MP23 microprocessor is designed to meet the demands of industrial, IoT, and edge AI applications.
Read more...
High-speed Flash for system-on-chip applications
NuVision Electronics
DSP, Micros & Memory
GigaDevice unveiled the GD25NE series of dual-power supply SPI NOR Flash chips, designed specifically for 1,2 V SoC applications.
Read more...
Ultra-low-power Arm Cortex MCU with FPU
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
STMicroelectronics expanded its STM32 ultra-low-power family with the launch of the STM32U3 for cost-sensitive applications in industrial, medical, and consumer electronics devices.
Read more...