

By far the biggest safety challenge in smoke detection is the saving of lives. Innovations in the smoke detection market have been driven by factors that include the following:
• Growth in industrial buildings: The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that the floor area of buildings globally is set to grow at approximately 3% per year. This is a result of increasing urbanisation and improved access to energy in developing countries.
• The increasing use of synthetic material within buildings.
This is why smoke detection regulations are critically important when the value proposition is as basic as human life itself. There are two predominant smoke detection technologies used in smoke detector systems:
• Ionisation systems.
• Photoelectric smoke detectors.
Here are some of the pending and current global standards and what they mean for smoke detection technology and markets.
A summary of global standards
There are basically five main global standards with different requirements to pass the respective certification. Smoke detector systems need to be fully tested as an end-product, but testing can also happen at the subsystem level. This does not substitute for full certification, but can give peace of mind before embarking on costly end system certification.
US and Canada
• UL 268: Smoke Detectors for Fire Alarm Systems.
7th edition: This was due to come into effect on 29 May 2020, although it may be delayed until 30 June 2021.
• UL 217: Smoke Alarms.
8th edition: This was due to come into effect on 29 May 2020, although it may be delayed until 30 June 2021.
These standards include updates to the polyurethane flaming and smouldering and cooking nuisance (hamburger) tests.
Europe
• EN 14604: Smoke Alarm Devices (2006).
• BS EN 54: Fire Detection and Fire Alarm Systems (2015).
Part 29: Multisensor fire detectors, these are point-type detectors using a combination of smoke and heat sensors.
International
• ISO 7240: Fire detection and alarm systems (2018).
Part 7: Point-type smoke detectors using scattered light, transmitted light, or ionisation.
The Chinese standard for point-type smoke detectors follows the 2003 edition of this standard.
Details on testing
There are two aspects to each standard, the tests and the requirements for test setup.
Fire room tests are expressed in terms of time to alarm after initiation of fire or in terms of obscuration levels (or in some cases both). Obscuration is a unit of measurement for the concentration of smoke. It measures the amount of light that reaches the detector in the presence of smoke compared to the amount of light that reaches the detector in clean air. The higher the value of obscuration, the higher the smoke concentration levels will be.
The most stringent testing standards are currently NA/Canada UL 217 and UL 268.
Some of the relevant tests are given below, but there are many more.
UL 217 (8th edition)/UL 268 (7th edition)
• Paper fire: Must give an alarm before t = 240 s.
• Wood fire: Must give an alarm before t = 240 s.
• Smouldering smoke: Must give an alarm before obscuration levels exceed 29,26%/m.
• Flaming polyurethane foam: Must give an alarm before obscuration levels exceed 15,47%/m and t = 360 s.
• Smouldering polyurethane: Must give an alarm before obscuration levels exceed 34,3%/m.
• Hamburger (nuisance alarm): Must not give an alarm/fault before obscuration levels exceed 0,987%/m or the MIC value is in the 59,3% to 49,2% range.
• Sensitivity test, dust test, high humidity test: Must not give an alarm/fault. The sensitivity test measures the obscuration level at which the unit alarms in a controlled smoke chamber.
• Flammable liquid fire (UL 268 Canada only). Must give an alarm before t = 240 s.
For EN 14604, BS EN 54 and ISO 7240, there can be different sensitivity levels on the same test or additional specifications pertaining to, for example, liquid (heptane) fire, glowing smouldering cotton, or low temperature, black smoke liquid fire.
For a complete set of tests, the relevant specification must be referenced in full.
Smoke detection technology: one size does not fit all
Each international region has a very detailed set of tests that have different methods and setups for testing.
Passing UL 217 and UL 268 standards − currently the most stringent two standards − can give a good indication of compliance, although this is not a substitute for regional testing.
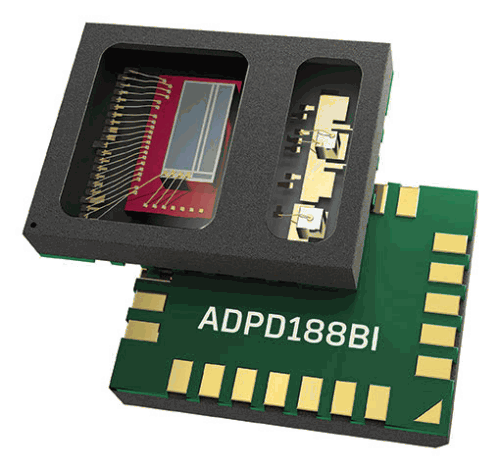
Using a component or subsystem that is UL-listed gives peace of mind. UL component recognition means that UL has evaluated components or materials intended for use in a complete product or system. These components are intended only for end-use products that may be eligible for UL certification. The ADPD188BI plus smoke chamber is currently pending for UL listing.
The ADPD188BI smoke detection module integrates LEDs, a photodiode and an analog front end (AFE) in one small 3,8 mm × 5,0 mm × 0,9 mm package. The benefits include:
• A reduced component count.
• Meets new and existing regulations for life safety due to a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and wide dynamic range for lower signal measurement.
• Reduced nuisance alarms to ensure verified alerts (and avoid alarm disable) by having two-colour detection and high dynamic range.
• Low power dissipation to allow more devices on wired or wireless loops.
• Small size to enable placement of detectors in hard to reach places.
• The elimination of LED supply chain management requirements.
• Running on a standard SMT assembly process.
The future
Regulatory changes have driven the trend toward smaller, more accurate smoke detection systems. In addition to the regulatory changes, customers are demanding better aesthetics and a wider range of trickier deployment scenarios. Meeting this demand will require smaller form factors at lower power.
About the author
Grainne Murphy is a marketing manager in ADI’s Intelligent Buildings Group. She is a University of Limerick, Ireland graduate (B.Eng) and holds an MBA from Oxford Brookes University. She can be reached at [email protected].
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved