
1-Wire networks are designed for communication with a single 1-Wire host and numerous 1-Wire nodes on a single 1-Wire bus. Preferably, a linear topology, which contains insignificant stubs, is best for a 1-Wire network. However, a star topology, which contains long stubs, is often unavoidable, and makes it more difficult to determine the effective limitations. A method to eliminate these difficulties is to break up a star topology into numerous channels by using an analogue multiplexer (mux).
Advantages of using numerous channels include accelerating individual 1-Wire node access time, improving network robustness, and mixing overdrive-only nodes with standard/overdrive nodes on different channels. These advantages can be gained, while still having a single 1-Wire host.
Arrangement
When configuring a 1-Wire network to have many channels, the general approach taken uses an Analog Devices’ 1-Wire host connected to the common signal of an analogue mux. The mux has digital channel select signals to connect the 1-Wire common signal to the desired I/O that contains a channel of 1-Wire node devices. With this arrangement, many more 1-Wire nodes can be networked over the limitations of a single 1-Wire bus. This is due to the elimination of stubs, and a decrease in the number of 1-Wire nodes per channel driven by the 1-Wire host.
Examination
Figure 1 shows a 3,3 V system when using the DS2485 1-Wire host. The microcontroller controls both the DS2485 and the mux channel to be selected. In a 1-Wire network, it is critical that the mux used can handle rail-to-rail analogue signals. Otherwise, signal distortion can occur and the VPUP parameter requirement of the 1-Wire nodes can be violated. The mux RON parameter must also be as small as possible to avoid altering the DS2485 active pull-up impedance (RAPU). If this is not taken into account, the 1-Wire nodes might not receive the necessary current to operate during a strong pull-up event.
Optionally, the mux (U2) has external, post-mux, pull-up resistors (RP4 and RP5) to provide power for idle 1-Wire nodes when the switches are open. If this is not done, each time a channel switch is connected, the microcontroller must wait the maximum wake-up time of the connected nodes on that channel (usually 2 ms) before beginning communication. However, it is important to consider the effects of the mux’s RON parameter during a pulldown event by the 1-Wire host when using an external pull-up resistor on each channel. Any effects can be considered negligible by selecting a small RON to avoid violating the highest 1-Wire input low parameter of the 1-Wire nodes. So, for a given post-mux pull-up resistor of RP and a given mux resistor of RON, the post-mux output low voltage is expressed using equation 1:
Additionally, it is important to consider the flexibility of the 1-Wire host used. Analog Devices recommends the DS2485 1-Wire host for any 3,3 V system because the DS2485 timing, input triggering levels, and internal pull-up resistors are very adjustable. The DS2485 can also be set to a high impedance mode, which can be helpful when using the external resistor option. However, if a system needs 5 V, then the next best option is to use the DS2484.
Lastly, during this examination, some systems require a mix of overdrive-only and standard/overdrive 1-Wire node devices. If the overdrive-only and the standard/overdrive devices reside on the same 1-Wire bus, communication faults occur. One simple solution is to use a mux that places overdrive-only devices on different channels than the overdrive/standard devices. The DS2485 can then simply switch to overdrive mode or standard mode between the selection of channels for proper communication.
Analogue Mux Selection
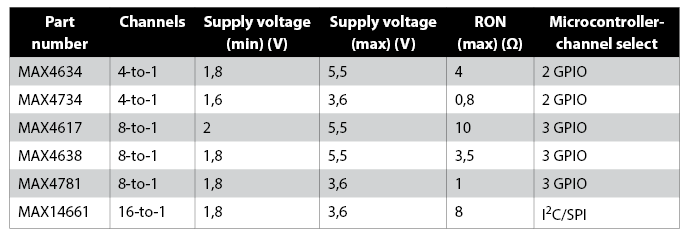
There are many requirements a designer considers when selecting the analogue mux. These requirements can be the number of channels, interface type, cost, package type, and performance. Table 1 lists the recommended analogue muxes for 1-Wire applications. All the recommended analogue muxes handle rail-to-rail analogue signals, have a small RON, and come in various package types.
The microcontroller that controls the selected channel must have spare GPIO pins. If the microcontroller does not have any spare GPIO pins, it is possible to use the MAX14661 or a similar device that can be tied to the same I2C bus used by the DS2485.
Conclusion
This article provides a method to break up star topography 1-Wire networks by using an analogue mux from the recommended list. As with the selection of any electronic component, the supporting system should carefully examine all device specifications under all use conditions to ensure reliable operation.
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved