
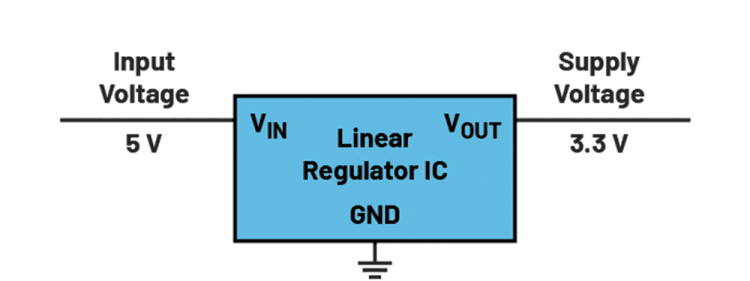
Linear regulators convert a higher voltage into a lower voltage. This generated voltage is precisely regulated to an adjustable value. In this way, supply voltages for a wide variety of applications can simply be generated.
However, due to their relatively low efficiency, linear regulators have been replaced with switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) in many applications. Figure 1 shows a simple linear regulator circuit for voltage conversion.
In recent years, linear regulators have found new main applications, particularly in supply line filtering. Figure 2 shows a passive filter option utilising an LC filter, which consists of a capacitor and a coil. This type of filter is preferred due to its low direct current (DC) losses, primarily attributed to the series resistance (DCR) of the coil L. Figure 2 shows such an LC filter.
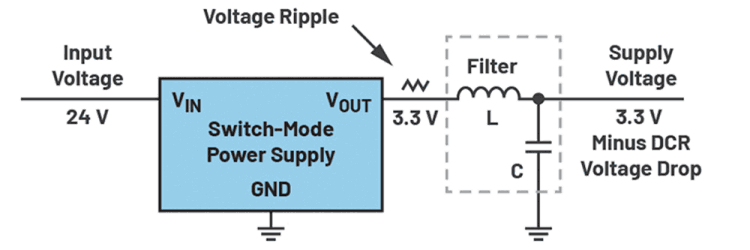
The effectiveness of this filter depends on its transfer function, characterised by the double pole position in the Bode plot. The gain decreases at 40 dB per decade from the corner frequency, determined by the values of L and C. This filter acts as a low-pass filter, allowing DC voltages to pass through, while attenuating higher frequency interference, such as voltage ripple on the supply line.
Unlike active circuitry, this filter does not require active components, but relies on a coil and a capacitor. Depending on the necessary current rating and inductance of the coil, it can be quite costly.
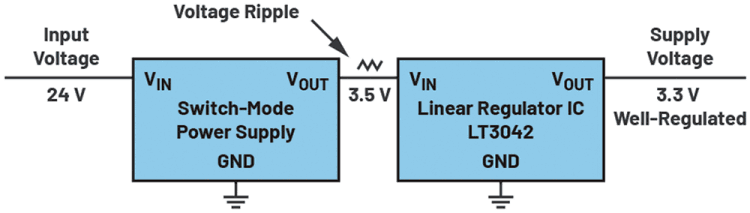
Figure 3 shows a linear regulator used as a filter to minimise the voltage ripple of an SMPS. The effectiveness of this filter depends on the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR), which is typically represented in a graph against frequency. A good PSRR value for a linear regulator is up to 80 dB attenuation at typical switching regulator frequencies of 1 MHz.
The LT3042 shown is a linear regulator, which is particularly suitable as a filter stage, as it offers a high PSRR even at high frequencies, and causes only very little interference of its own. This is especially important in applications where a filter is required to clean a supply voltage.
There are different ways to implement a filter, and one significant advantage of using a linear regulator for filtering is its precise regulation of the output voltage. An LC filter lacks its own voltage regulation loop, causing the generated voltage to be influenced by the behaviour of the original voltage source, such as an SMPS. Depending on the DC current flow through the LC filter (shown in Figure 2), the coil’s DCR can impact the output voltage to varying degrees. While this behaviour may be acceptable for applications with constant load current, it can pose challenges in applications with varying load currents.
Conclusion
To evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different filter implementations for specific applications, simulation tools may be highly beneficial. LTspice is a free and effective simulation tool that can assist in this process.
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved