
Settling a key dispute in the wireless communications field, researchers at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) found that transmission performance is consistent across different bands of the millimetre-wave (mmWave) spectrum targeted for high-speed, data-rich 5G systems.
Wireless systems are moving to the mmWave spectrum at 10-100 GHz, above crowded cellular frequencies as well as early 5G systems around 3 GHz. System operators tend to prefer lower bands of the new mmWave spectrum. One reason is that they are influenced by a formula that says more signals are lost at higher frequencies due to smaller wavelengths, resulting in a smaller useful antenna area. But until now, measurements of this effect by many organisations have disagreed over whether this is true.
NIST researchers developed a new method to measure frequency effects, using the 26,5-40 GHz band as a target example. After extensive study in the laboratory and two real-world environments, NIST results confirmed that the main signal path – over a clear “line of sight” between transmitter and receiver – does not vary by frequency, a generally accepted thesis for traditional wireless systems but until now not proven for the mmWave spectrum. The results are described in a new paper https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9759479.
The team also found that signal losses in secondary paths – where transmissions are reflected, bent or diffused into clusters of reflections – can vary somewhat by frequency, depending on the type of path. Reflective paths, which are the second strongest, and critical for maintaining connectivity, lost only a little signal strength at higher frequencies. The weaker bent and diffuse paths lost a bit more. Until now, the effects of frequency on this so-called multipath were unknown.
“This work may serve to demystify many misconceptions about propagation around higher frequencies in 5G and 6G,” NIST electrical engineer Camillo Gentile said. “In short, while performance will be worse at higher frequencies, the drop in performance is incremental, so we do expect the deployment at 5G and eventually at 6G to be successful.”
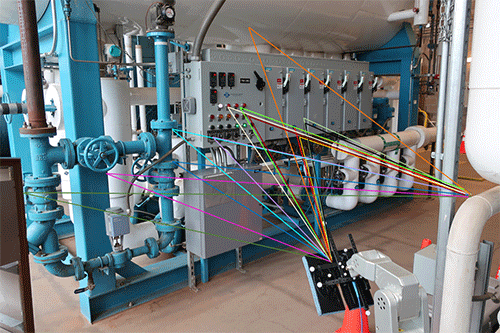
The NIST method emphasises innovative measurement procedures and enhanced equipment calibration to make sure only the transmission channel is measured. The researchers used NIST’s SAMURAI (Synthetic Aperture Measurement UnceRtainty for Angle of Incidence) channel sounder, which supports design and repeatable testing of 5G mmWave devices with unprecedented accuracy across a wide range of signal frequencies and scenarios. The NIST system is unique in that antenna beams can be steered in any direction for precise angle-of-arrival estimates.
NIST’s main innovations in the new study, as discussed in the paper, were calibration procedures to remove the effects of channel sounder equipment from the measurements, extension of an existing algorithm to determine from a single measurement how individual paths vary by frequency, and studies in an industrial control centre and a conference room to classify the types of paths involved and determine any frequency effects.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved