
The term Internet of Things (IoT) is used to describe the practice of connecting devices through the use of the Internet. The IoT is already connecting computing devices, appliances, humans and other living beings through the In-ternet. Accumulating data and knowledge through these Things would improve a vast array of items and experiences throughout the world. The IoT is made of events and signals of many different kinds and requires a standardised mode of communication.
In a report published by IBM on the future of the Internet of Things, the number of connected devices is forecast to surpass 30 billion in 2020, up from 2,5 billion in 2009 and 10 billion today. The connected devices need a protocol with which to communicate only when it is required. Devices with constrained resources should be able to communicate with various other heterogeneous devices.
MQ Telemetry Transport Protocol (MQTTP or simply MQTT) is described on the mqtt.org website as a machine-to-machine (M2M) / IoT connectivity protocol. This protocol is so lightweight that it can be supported by some of the smallest measuring and monitoring devices, and it can transmit data over far reaching, sometimes intermittent networks.
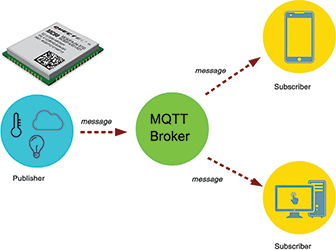
MQTT is a publish/subscribe messaging transport protocol that is optimised to connect physical world devices and events with enterprise servers and other consumers. It is designed to overcome the challenges of connecting the rapidly expanding physical world of sensors, actuators, phones and tablets with established software processing technologies. These principles also turn out to make this protocol ideal for the emerging M2M or IoT world of connected devices where bandwidth and battery power are at a premium. The following are the five most important things to know about MQTT protocol.
MQTT publish subscribe architecture
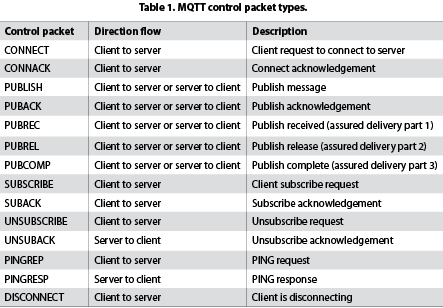
The MQTT messages are delivered asynchronously (‘pushed’) through publish subscribe architecture. The protocol works by exchanging a series of MQTT control packets in a defined way. Each control packet has a specific purpose and every bit in the packet is carefully crafted to reduce the data transmitted over the network. An MQTT topology has a server and a client, each of which communicates through different control packets. Table 1 briefly describes each of these control packets.
Ideal for constrained networks
MQTT control packet headers are kept as small as possible. Each MQTT control packet consists of three parts: a fixed header, a variable header and a payload. Each packet has a 2 Byte fixed header, while not all packets have the variable headers and payload. A variable header contains the packet identifier if used by the control packet. A payload up to 256 MB could be attached in the packets.
Having a small header overhead makes this protocol appropriate for IoT by lowering the amount of data transmitted over networks constrained by factors like low bandwidth, high latency, data limits and fragile connections.
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) levels determine how each MQTT message is delivered, and must be specified for every message sent. It is important to choose the proper QoS value for every message, because this value determines how the client and the server communicate to deliver the message. Three QoS for message delivery could be achieved using MQTT:
• QoS 0 (At most once) – where messages are delivered according to the best efforts of the operating environment. Messages loss can occur.
• QoS 1 (At least once) – where messages are assured to arrive but duplicates can occur.
• QoS 2 (Exactly once) – where message are assured to arrive exactly once.
There is a simple rule when considering the performance impact of QoS, namely ‘the higher the QoS, the lower the performance’. MQTT provides flexibility to the IoT devices, to choose the appropriate QoS they would need for their functional and environment requirements.
Abnormal disconnect notification
When an MQTT client connects to the MQTT server it can define a topic and a message that needs to be published automatically on that topic when it unexpectedly disconnects. This is also called the ‘Last Will and Testament’ (LWT). When the client unexpectedly disconnects, the keep alive timer at the server side detects that the client has not sent any message or the keep alive PINGREQ, hence the server immediately publishes the Will message on the Will topic specified by the client.
The LWT feature can be useful in some scenarios. For example for a remote MQTT client, this feature can be used to detect when the IoT device goes out of the network. The LWT feature can be used to create notifications for an application that is monitoring the client activity.
Clients are very simple to implement
MQTT is an open protocol, standardised by the OASIS Technical Committee. This makes it easy to adopt for the wide variety of IoT devices, platforms and operating systems. Many applications of MQTT can be developed just by implementing the CONNECT, PUBLISH, SUBSCRIBE and DISCONNECT control packets. A variety of MQTT client libraries are made available through the Eclipse Paho project. Eclipse Paho MQTT client libraries can be downloaded from www.eclipse.org/paho
The IBM MessageSight messaging appliance helps to deliver the performance, value and simplicity that organisations need for accommodating this multitude of devices and processing large volumes of events in real-time. IBM MessageSight is built from the ground up with new technology to provide high scalability, and extends existing messaging networks by adding fast transaction rates, consistently lower latency, and extensive scaling in the number of concurrent devices that can be connected. It is also suitable for deployment in a demilitarised zone (DMZ).
In summary, MQTT is a protocol built for M2M and IoT which can help provide revolutionary performance, and opens up new areas for messaging use cases for billions of things connected through the Internet. The IBM Redbooks publication ‘Building Realtime Mobile Solutions with MQTT and IBM MessageSight’ covers the theory and real-world scenarios for using MQTT along with IBM MessageSight for mobile and other Internet of Things applications.
| Tel: | +27 11 781 2029 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.icorptechnologies.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about iCorp Technologies |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved