
Applications requiring sub-ten-meter positioning accuracy today can choose between single-band or dual-band technology. While this decision might seem as simple as flipping a coin, it is far from that. Designers must carefully weigh their choice, as it can significantly impact the end user application. Power consumption, costs, required accuracy, and the environment in which the application is used are the key factors designers should consider before opting for one or the other.
The major difference between single-band and dual-band GNSS receivers lies in the frequency bands they use to receive data. Single-band GNSS receivers rely on a single frequency band, typically the L1 band. In contrast, dual-band receivers utilise two bands, usually L1 and L2 or L1 and L5.
This fundamental difference impacts position accuracy, particularly in multipath environments, as they can be an urban area or a tree-covered region. The choice between the two thus depends on the specific purpose and requirements of the application.
Open-sky environment
Suppose your end user application is designed for people/asset tracking, a consumer UAV, all of which typically require sub-ten-meter position accuracy. In this case, devices are usually battery-powered and should consume minimal power to last a considerable amount of time without the need to recharge them.
Since L1 single-band receivers are more affordable due to their use of common RF components, straightforward antenna designs, and lower power consumption compared to dual-band receivers, they are a good option for the mentioned applications mainly operating in open sky conditions or with high battery constraints.
In an open-sky environment, these applications will operate similarly to those with dual-band receivers. For instance, if a company is tracking a truck or a rental car moving on highways of a country, single-band receivers could be the right choice.
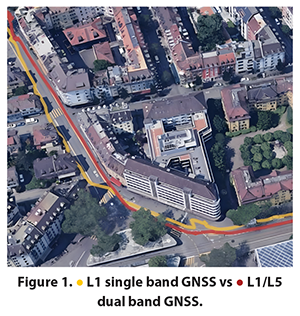
Urban areasMicromobility and wearable applications have one thing in common; both require good performance in urban areas, where large buildings, tunnels, bridges, and other obstacles, such as trees, can reflect satellite signals. In this environment, a single-band receiver may not suffice. Instead, you would need an L1/L5 dual-band GNSS receiver, which can offer good positioning accuracy, even in this setting where applications need to be resilient to multipath effects, while providing meter-level positioning.
However, there are drawbacks to dual-band receivers. They consume more power than single-band receivers, which can pose challenges for battery-powered devices. Another important aspect to note is that the GPS L5 signal is currently not fully operational.
High position availability
Some high-end aftermarket telematics applications do not only ask for good position accuracy, but also for high position availability. For example, when the vehicle enters a covered parking area. In such cases, it is possible to combine GNSS technology with dead reckoning. The combination offers further advantages, including continued navigation with GNSS outages, which typically occur in tunnels or underground parking areas.
Choosing a GNSS product
L1 single band GNSS products like the u-blox M10 and the L1/L5 dual-band GNSS products like the u-blox F10 are a good starting point for most use cases.
| Tel: | +27 21 555 8400 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.rfdesign.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about RF Design |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved