
Accutronics represents several manufacturers of products for RF and microwave transmission applications. One of these companies, Narda Safety Test Solutions (Narda-STS) is a manufacturer of radiation monitoring equipment, used specifically to monitor non-ionised radiation.
Electromagnetic radiation
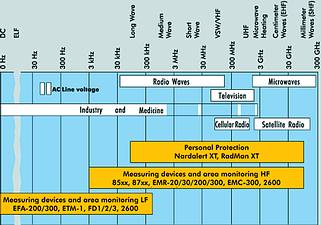
Non-ionised radiation covers the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum from DC to 300 GHz and then the light spectrum to above ultra-violet, after which it becomes ionising radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is essentially caused by any electrically-driven instrument, and is, of course, generated intentionally in communication systems.
Typical industrial applications with commonly high EM radiation levels are: metal welding, heating and hardening; plastics manufacturing, moulding, welding and lamination; electrical power distribution. Typically, this radiation is found in the vicinity of the instrumentation, but it may also cover a fairly big area depending on the levels and its relatively low frequency.
Typical communications applications with potentially high EM radiation levels:
* All communication systems (HF, VHF and UHF bands/radio, television, CB, etc).
* Cellular from 900 MHz to 2,7 GHz (base stations, repeaters and cellular handsets).
* Satellite (typically in band segments between 2 to 30 GHz).
* Radar systems (commercial and military).
The transmissions are typically in the form of fixed directional (eg, repeaters, satellite base stations), swept directional (eg, radars) and omni-directional (eg, cellular base stations and repeaters). Therefore the levels of environmental exposure to such transmissions may be limited, depending on antenna-patterns.
The term 'electromagnetic' refers to two components - an electrical field/plane and magnetic field/plane. Both fields have individual dangers associated with them, and also combined dangers. The electrical field has good propagation properties in free-space (and many materials), but is easily shielded against (eg, grounded metal foil). The magnetic field penetrates almost any material, but is generally more of a 'close-range' danger.
Due to these properties of the magnetic field in particular, electromagnetic radiation is generally categorised into a near field and far field. As a rule, the near field is deemed less than 3 x wavelength and the far field is above 3 x wavelength. [wavelength = c/f, (where c is the speed of light ~ 300 000 000 m/s and f is the frequency of reference in Hz)].
In the near field, the electrical and magnetic components carry no relationship in terms of field strength and must therefore be measured individually, especially as the magnetic field is typically very high. However, in the far field a relationship exists between the two components and it is really only necessary to measure one component. As the electrical field is now much more prominent (E = H x 377 Ω), it is typically this component that is measured.
Generally the effects of electromagnetic radiation on the human body can be categorised according to frequency - as low-frequency (LF) being from DC (0 Hz) to 32 kHz, and high-frequency (HF) being anything greater than 32 kHz. With this, the effects of LF are: low levels - subtle changes in the body's calcium metabolism have been noted; medium - changes in protein and DNA synthesis, and evident nerve effects; high - the excitability of the central nervous system is changed; very high - severe heart dysfunction and acute dangers to one's health. The effects of HF are: the areas of the body with the least blood flow (bone structure, eyes, etc) are most endangered. The body is heated by the radiation, with the obvious effect being burns. May also cause blindness, various types of cancer, hormonal changes, stunted cell growth and may have an effect on the immune system.
Studies
The concerns as to the possible effects were raised to a high level during the 1990s, with several studies conducted. This led to various standards being created to attempt to control and limit the exposure to this radiation. In Europe the International Commission for Non-Ionised Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) was created and in April 1998 the standard 'Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz)' was published. This standard has been widely accepted and applied.
In South Africa, the Department of Health has a division called the Directorate: Radiation Control. It has selected the ICNIRP-standard for use in South Africa, and has also published a document, with the same name, based on the ICNIRP-guideline.
The Department of Health is responsible for administering the hazardous substances Act, 1973 (Act 15 of 1973), which may include most high-power electrical systems and most transmission equipment. According to the Act, any person who wishes to import or manufacture such devices has to obtain a licence in terms of section 4(i) (b). This licence is issued if the product complies with the internationally recognised requirements for safety and performance. Should such a licence be required and consequently be issued by the Department of Health, then conformity to the document 'Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz)' of the Directorate: Radiation Control, becomes a legal requirement. If no legal requirement for conformity exists, the document is merely a guideline, with pro-active control of radiation being the key.
Ultimately, apart from any possible legal requirements, it is always wise to be pro-active and ascertain whether a possible radiation hazard does exist for both employees and communities in the surroundings of any potentially hazardous equipment. Accutronics is able to assist with information on radiation monitoring equipment and techniques.
For more information contact Tobie Muller, Accutronics, 011 463 2287.
| Tel: | +27 11 782 8728 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.accutronics.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Accutronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved