Tech note: How to use a FET to overcome the input voltage limitation of a linear regulator
2 June 2004
Power Electronics / Power Management
Jeff Falin, Texas Instruments
All integrated circuits have an input voltage limitation due to the manufacturing process. This limitation is cumbersome when trying to step down a high-supply voltage to a lower, regulated voltage using a DC/DC converter such as a linear regulator. Adding a FET to the input of a linear regulator creates a DC/DC converter with a wider input voltage range than the range of the regulator alone. The excess voltage (and therefore power) is dropped across the FET.
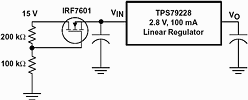
Figure 1 shows an IRF7601 N-channel MOSFET on the input of a TPS79228 2,8 V, 100 mA, low-noise, high-PSRR LDO regulator. The two resistors provide a bias voltage to the gate of the MOSFET and the load current determines the voltage at the source of the MOSFET (ie, the FETs on resistance adjusts to meet the load current). The MOSFET is selected based on three criteria: drain to source breakdown voltage, gate drive requirements, and power dissipation capabilities. In this example, the maximum power-supply voltage is 15 V, but the TPS79228 has a maximum recommended operating input voltage of 5,5 V, so a MOSFET with a 20 V breakdown voltage is selected.
Figure 1. MOSFET switch used to expand the regulator’s input voltage
To determine the minimum bias voltage for the gate of the MOSFET, the MOSFET's drain current (ID) vs gate-source voltage (VGS) data sheet curve is required. For the IRF7601, the curves indicate that the device needs VGS slightly below 1,5 V for a 100 mA output current. Since the maximum dropout of the regulator is 100 mV at 100 mA, the regulator's input voltage must stay above 2,9 V. Therefore, the gate of the MOSFET must be biased to at least 1,5 V + 2,9 V = 4,4 V, so that when the MOSFET is providing 100 mA, its source voltage does not drop below 2,9 V. The maximum gate bias voltage is simply the maximum recommended operating voltage for the regulator, or 5,5 V. This voltage provides more than enough gate drive to provide the regulator's 1 µA of quiescent current while in shutdown mode.
Although the gate can be biased between 4,4 V and 5,5 V, a bias voltage of 5,0 V is selected to account for variations in the threshold voltage. Maximum power dissipation for the FET is:
100 mA x (15 V - 2,9 V) = 1,21 W
which the IRF7601 in a Micro 8 package can handle for TA = 55°C.
So, a low noise, low ripple 2,8 V output voltage is generated from a 15 V supply using the TPS79228 and a MOSFET.
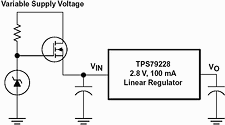
Figure 2 is slightly more complicated but may be necessary if the input voltage varies significantly. A Zener diode replaces the bottom resistor in Figure 1 and provides a fixed gate drive to the MOSFET. The output voltage of the Zener is selected in a manner similar to that explained previously.
Figure 2. MOSFET switch biased with Zener diode used to expand regulator’s input voltage
Summary
Either method is acceptable for creating a DC/DC converter with a wider input voltage range than the converter IC allows. The single MOSFET solution is the simplest and cheapest solution. The MOSFET biased with a Zener diode is the best choice when the supply is unregulated.
Further reading:
ABB’s Mission to Zero drives South Africa’s energy transition
ABB Electrification Products
Power Electronics / Power Management
ABB Electrification is charting a bold path towards a net-zero future with its Mission to Zero programme, a blueprint that combines energy efficiency, electrification, and digital innovation to accelerate the transition to clean energy.
Read more...
Energy harvesting using a battery-less IoT system
NuVision Electronics
Editor's Choice Power Electronics / Power Management
Energy Harvesting plays an essential role in the foundation of ambient IoT, a new generation of ultra-low power connected devices that operate by drawing energy from their environment instead of relying on traditional batteries.
Read more...
Driving power, defining performance
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
Vishay’s portfolio of inductors, current sense resistors, and MOSFETs provides a comprehensive solution for intelligent power management.
Read more...
Battery simulator module simplifies BMS testing
Test Dynamics
Power Electronics / Power Management
The PXI/PXIe solution from Pickering Interfaces offers a scalable, modular design for faster development cycles, lower total cost of ownership, and improved safety.
Read more...
DC PSU: The cornerstone for efficient solar-storage systems
Vepac Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
PV energy storage systems are evolving and DC power supplies, with their technical characteristics that are naturally compatible with new energy, have become a key carrier for improving system energy efficiency.
Read more...
Why local manufacturing, maintenance and support are key to the success of South Africa’s energy future
Power Electronics / Power Management
Although new renewable generation capacity is being developed, the current transmission infrastructure may not fully support the connection of these sources to the national grid or adequately deliver power to areas of high demand.
Read more...
Converter power modules for 48 V networks
Altron Arrow
Power Electronics / Power Management
The economic and quality-of-life benefits of electrification is driving the adoption of HV to 48 V DC-DC conversion across many markets with 48 V power modules becoming more common.
Read more...
The importance of power integrity
Spectrum Concepts
Power Electronics / Power Management
[Sponsored] Behind every high-speed system lies the need for power integrity. Without it, even the cleanest signal paths become compromised.
Read more...
Precise multi-vital sign monitoring
Future Electronics
Power Electronics / Power Management
The AS7058 by ams OSRAM is an integrated multi-vital sign monitoring device, which provides a complete photoplethysmogram, electrocardiogram, body impedance sensor, and electrodermal activity sensor.
Read more...
Automotive battery diagnostics tester
Comtest
Power Electronics / Power Management
Midtronics’ MVT handheld battery tester is a revolutionary tool, powered by MDX-AI, which is set to redefine the standards of battery diagnostics and testing in the automotive industry.
Read more...