

ECE of Taiwan is a large manufacturer of DIP switches, photo-MOS relays, reed relays, terminal blocks, resettable fuses, USB connectors, and phone jacks etc.
Since its 1981 establishment, it has followed a pattern of continuous improvement by investing in top-of-the-line equipment, creating new products and improving its manufacturing procedures.
The company makes a range of polymer resettable fuses that are suitable for protection of electronic equipment that includes: computers, peripherals, security and fire alarm systems, general electronics, loud speakers, automotive applications and power transformers.
Polymeric PTC
Overcurrent protection can be achieved with either a traditional fuse or the PPTC (polymeric positive temperature coefficient) element. However, the key difference is that the PPTC is 'resettable', which means its resistance is able to be recovered. This allows it to be used again. PPTC elements compose of a polymer matrix and conductive materials. It protects the circuit by 'tripping' from a low resistance to an extremely high resistance state in response to an overcurrent (Figure 1).
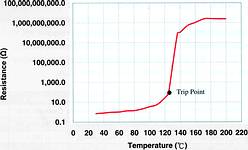
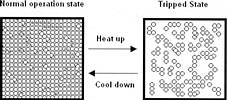
ECE offers a wide selection of resettable fuse construction types. The PPTC material's resistance increases as the temperature rises. Should a situation of overcurrent/overheating affect the device, it will begin to heat itself up and its polymer matrix will change from crystalline to amorphous (Figure 2). This change will dramatically increase the resistance of the PPTC, and so reduce the current flow in the circuit. After the fault is removed, the resistance recovers in a short time and it again operates under normal conditions.
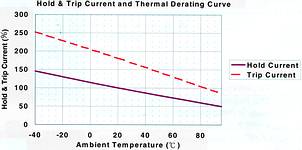
Hold/trip current and thermal derating
The maximum current at which the device will not trip is called the Hold Current (IH). The Trip Current (IT) is the minimum current at which the device will always trip. In ECE specifications these values are rated at a temperature of 23°C. The temperature derating curve in Figure 3 clearly indicates that both IH and IT decrease, while ambient temperature increases.
Selecting the right PTC fuse
1. Determine product type (radial, axial, SMT) based on application and circuit.
2. Confirm operating voltage, current, max operating voltage, max interrupt current, and max ambient temperature to protect your circuit.
3. Refer to the electrical characteristics table and thermal derating curve to choose the appropriate resettable fuse.
4. Ensure the circuit's max operating voltages and currents are below the standard of the selected resettable fuse.
5. Verify the time-to-trip curve and make sure the resettable fuse is capable of protecting your circuit in time.
6. Check that the dimension of the fuse is suitable for your circuit.
7. Finally, test and make sure of the suitability of the selected resettable fuse.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved