Murata-pioneered navigation sensors
22 September 2004
Passive Components
Information from Avnet Kopp
Ref: z2717151m
Satellite navigation systems are great when they can 'see' the satellite, but they need a temporary reference when they cannot. One of the best available solutions currently is Murata's ceramic bimorph gyroscope technology. However, car navigation systems require higher accuracy than, say, video cameras and the like. Therefore, Murata has increased the processing accuracy of the bimorph vibrator and devised a new structure that produces more stable vibration.
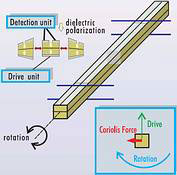
With tuning bar piezoelectric gyroscopes, the bar is vibrated by piezo-electric ceramics. When rotational motion is applied to the centre axis of the vibrator, a Coriolis force is generated perpendicular to the original direction of vibration. This force is detected by more piezoelectric ceramics.
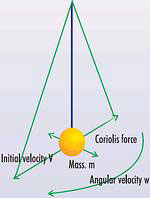
The principle used for detection is as follows: taking the Foucault pendulum, (shown in Figure 1) when angular velocity 'w' is applied to the axis of an object of mass 'm' swinging at velocity 'V', a Coriolis force expressed by formula: F = 2m V X w is generated.
Figure 1
This force is perpendicular to the reciprocating motion of the pendulum, being largest at the highest velocity point. Generally, the magnitude of angular velocity can be measured by electrically detecting the Coriolis force while keeping 'V' constant. Murata's original structure was triangular, with numerous micron-diameter lead wires making interconnections.
This has been changed to a rectangular cross-section needing no interconnections, reducing size while improving production efficiency and performance. The latest version is smaller, with a plate inserted into the bottom of the vibrator section to provide more stable vibration, giving better frequency stability.
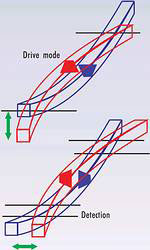
Electrical bonding and mechanical support have recently been improved by a new process. Figures 2 and 3 show the principle of operation.
Figure 2
Figure 3
The net result of this work is the ENV-05G, a bimorph gyroscope that is ideal for car navigation systems. The new design is much more accurate and easier to produce. In a 12,4 by 7,6 mm package, 18 mm high, it has an operating temperature range of -40°C to 85°C, scale factor of 25 mV/°/s and offset drift of 9°/s. This sensor is specifically intended for measuring the position of moving objects, especially motor vehicles.
Further reading:
High-endurance polymer tantalum capacitors
Passive Components
Panasonic Industry TDC Series POSCAP polymer tantalum capacitors deliver high endurance and reliable performance in demanding, high-temperature environments.
Read more...
Thin-film inductors for optical transceivers
RS South Africa
Passive Components
TDK has expanded its PLEC69B series (1,2 x 0,6 x 0,95 mm – L x W x H) of thin-film inductors, used for separating the data signal from the power in optical transceivers in AI data centres.
Read more...
Low-resistance MLCCs
RS South Africa
Passive Components
TDK Corporation has expanded its CN series of low-resistance soft-termination multilayer ceramic capacitors; achieving 22 nF capacitance in the 3225 case size.
Read more...
Ferrite cores with different shapes
RS South Africa
Passive Components
TDK Corporation has introduced a variety of new large-size ferrite cores with different core shapes, making this the industry’s largest lineup of shapes, sizes, and materials for such large cores.
Read more...
Vibration-resistant axial capacitors
RS South Africa
Passive Components
TDK Corporation has unveiled the B41699 and B41799 series of ultra-compact aluminium electrolytic capacitors, engineered to withstand operating temperatures of up to 140°C.
Read more...
Capacitors for demanding industrial applications
Passive Components
TDK Corporation has announced its X1 capacitors of the EPCOS B3291xH/J4 series for power line filtering of electromagnetic interferences in demanding automotive and industrial applications with a rated AC voltage of up to 480 V.
Read more...
Wide frequency range inductors
RS South Africa
Passive Components
TDK Corporation has expanded its ADL4524VL series
(4,5 x 2,4 x 2,6 mm – L x W x H) of wire-wound inductors for automotive power-over-coax.
Read more...
Cutting-edge hybrid capacitors
Avnet Silica
Passive Components
Panasonic Industry recently announced the launch of the ZVU Series Hybrid Capacitors, a cutting-edge solution tailored to meet the escalating demands of advanced electronic systems.
Read more...
Low-profile tantalum chip capacitors
Electrocomp
Passive Components
These general-purpose tantalum capacitors from Kyocera AVX are available in multiple case sizes with low profile options.
Read more...
Coupled inductor for high-performance applications
Passive Components
This coil with MnZn core is characterised by its high permeability and extremely low RDC values, which achieves excellent power density and very high efficiency.
Read more...