
Recent sensor technology developments are enabling revolutionary improvements in industrial system designs. Applications where inertial sensors can potentially improve system performance include platform stabilisation, motion control for industrial machinery, security/surveillance devices, robotics, industrial vehicle navigation and mechanical levelling.
The motion information provided by such sensors can be invaluable in improving not only performance but also reliability, safety and cost of ownership.
However, there are barriers to overcome to obtain these benefits, particularly in the tough physical environment of many industrial applications, where temperature, vibration, limited space and other factors must be addressed. Extracting consistent data from the sensor, translating it into useful information, and reacting to it within the system’s timing and power budget require expertise on the part of the engineer in many technology domains, including careful design practice.
Understanding the problem
Information from inertial sensors can be processed and integrated to derive many different types of motion, position and directional outputs. Each type of motion entails a wide range of application-dependent complexities that must be understood. A good example of this is industrial control applications where some form of pointing or steering of equipment is useful. Tilt or angular sensing is often at the heart of such applications and, in its simplest incarnation, a mechanical bubble or ball in tube sensor may suffice.
However, before specifying the sensor requirements, the full motion dynamics, environment, life cycle and reliability expectations of the end system must be analysed. If the system’s motion is relatively static, a simple angle sensor may be adequate; but response time, shock and vibration, size and performance drift over life will drive the actual technology decision. Additionally, many systems involve more than one type of motion (rotation plus acceleration, for instance) and quite often operate on more than one axis, thus driving the need to consider combining multiple sensor types.
Once the proper sensor types and technology are known, the challenge shifts to understanding, and ultimately compensating for, the sensor’s reaction to the environment (temperature, vibration, shock, mounting position, time and other variables). Such environmental compensations involve additional circuitry, testing, calibration and dynamic adjustments. Because every sensor type, and ultimately every sensor, is unique, there is the added risk of under- or over-compensating unless sensor characteristics are fully understood. This last point is what drives many designers to adopt more fully integrated sensor solutions that can reduce the barriers to adoption and implementation.
Linear rate and angular rate sensors
There are several kinds of inertial sensors. MEMS (micro electromechanical system) sensor technology is among the most well established and has brought benefits to a wide range of applications. MEMS linear rate sensors (accelerometers) revolutionised the automotive airbag system industry 15 years ago. Since then, they have enabled unique features and applications ranging from hard disk protection on laptops to more intuitive motion capture in game controllers.
Angular rate sensing is also available from MEMS structures based on the principle of a resonator gyro. Two polysilicon sensing structures each contain a dither frame which is electrostatically driven to resonance. This produces the necessary movement to create a Coriolis effect during rotation. At two of the outer extremes of each frame, orthogonal to the dither motion, movable fingers are placed between fixed fingers to form a capacitive pick-off structure that senses Coriolis motion. When the MEMS gyro is rotated, the change in position of the movable fingers is detected via a change in capacitance, and the resulting signal is fed to a series of gain and demodulation stages that produce the electrical-rate signal output. In some instances, the signal is then converted and fed into a proprietary digital calibration circuit.
The level of integration and calibration around the sensor core is dictated by the end performance requirements but, in many cases, motion calibration may be desired to achieve the highest level of performance and stability.
Integrated signal conditioning and sensor processing
In the industrial market, applications such as vibration analysis, platform levelling and general motion control need highly integrated and reliable solutions where, in many cases, the sensing element is embedded directly into the existing equipment. It is also important to provide sufficient control, calibration and programming features to make the device truly self-contained. Some applications examples include:
* Condition monitoring of industrial machinery: substantial value can be gained from the ability to more deeply embed sensors within machinery and to get an earlier and more accurate representation of condition shifts related to both sensor performance and embedded processing.
* Machine automation: autonomous or remotely controlled precision instruments and robotic arms can be made more accurate and efficient by improving accuracy and more tightly correlating them to remotely controlled or programmed movement.
* Mobile communications and surveillance: whether on land-, air- or sea-based vehicles, inertial sensors can aid both in stabilisation (antennas and cameras) and in directional guidance (dead reckoning with GPS and other sensors).
Because the industrial sensing market is incredibly diverse, it requires a wide range of performance, integration and interfaces that must be accommodated via the integration of embedded, tuneable features such as digital filtering, sample rate control, condition monitoring, power management options and application-specific auxiliary I/O functions.
In other, more complex scenarios, the use of multiple sensors and sensor types is also required. Even apparently simple inertial motion constrained to movement on one or two axes can require both accelerometer and gyroscope sensing to compensate for gravity, vibration and other irregularities and influences. Sensors additionally can have cross-sensitivities which, at a minimum, must be understood, and oftentimes compensated for. This is made more difficult by the varying standards for inertial sensor specifications.
When specifying inertial sensors, most industrial system designers are primarily concerned with gyro stability (bias estimation over time), which is typically not specified in consumer grade gyros. Even a good gyro bias stability of 0,003°/s is somewhat meaningless if the sensor has poor performance with respect to linear acceleration. A linear acceleration specification of 0,1°/s/G, for instance, adds 0,1° of error to the bias stability spec of 0,003°/s, in the simple environment of rotation through ±90° (1 G).
Typically, an accelerometer is used in conjunction with the gyroscope to detect the gravity influence and provide the necessary information to drive the compensation process. Optimising sensor performance and minimising development time require intimate knowledge of both sensor sensitivities and the application environment. The calibration plan can be tailored to address the most influential elements and thus minimise test time and compensation algorithm overhead. If made cost effectively and with standard, system-ready interfaces, application-focused solutions that combine the appropriate sensors with the necessary signal processing can remove the implementation and production barriers that many industrial customers have faced in the past.
Harnessing acceleration to provide vibration analysis
In some cases, the sensing element is optimally designed in relatively close to the basic transducer output, while in others (condition monitoring with vibration analysis), there is significant additional processing required to realise the desired output. An example of a highly integrated device built around an inertial sensor is the Analog Devices ADIS16227 (Figure 1), a fully autonomous frequency domain vibration monitor.
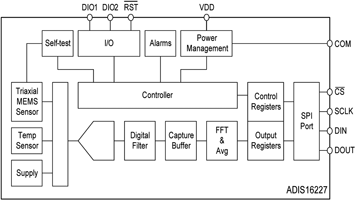
Rather than the relatively simple output of G/mv, devices like this may instead provide application-specific analysis – in this case, embedded frequency domain processing, a 512-point real value FFT and onboard storage, providing the ability to identify and classify individual sources of vibration, monitor their changes over time and react to programmable threshold levels.
The ability to detect and understand motion has the potential to add value to nearly any conceived application. In most cases, the desire is to harness the motion that a system experiences and translate that information into improved performance (response time, precision, speed of operation); enhanced safety or reliability (system shut-off in dangerous situations); or other added-value features.
In some cases, it is the lack of motion that is critical, and thus sensors can be used to detect unwanted movement. These feature or performance upgrades are often implemented on existing systems, and the small size and low-power aspects of MEMS inertial sensor components are attractive given that the end-system’s power and size envelope are obviously already fixed or must be minimised. In some cases, designers of these systems are not motion dynamics experts and thus the availability of fully integrated and calibrated sensors can be the critical go-ahead factor in choosing to proceed with these system upgrades.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved