
In the last few years, one of the most successful applications in the M2M (machine to machine) market has been the remote control of devices over GSM, and this kind of application will likely continue its strong growth in the years ahead.
Remote control is usually accomplished by sending commands to a remote module through DTMF tones or SMS. These commands allow remote driving of actuators and the reading of sensor status.
The newly released DTMF decoder in Telit modules allows developers to change their traditional approach when working with GSM remote control systems. Although a TCP connection mode is also available, this article will focus on the DTMF solution.
Traditional approach
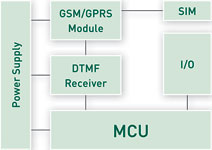
The traditional way to implement remote control via GSM using DTMF tones typically involves the use of a microcontroller (MCU), a GSM module and a hardware DTMF decoder (Figure 1). When DTMF tones are employed to send remote commands, the audio output from the GSM module is connected to the DTMF receiver which provides decoded tones to the MCU. The MCU in receipt of this information recognises the command and takes the appropriate action or sequence of actions. The Achilles heel of this approach is the need for several components to execute even the simplest command.
Telit’s approach
The aim of the Telit approach is to simplify the system by more fully utilising the powerful embedded features of the GSM module while at the same time giving new degrees of freedom to the developer (Figure 2). With this smart use of the Telit module, the DTMF receiver and the external microprocessor can be removed, leading to a smaller and cheaper implementation. In fact, DTMF tones are recognised by the internal decoder embedded in the module without the need for any external device (Figure 3).


Embedded DTMF decoder
To access this feature, developers can select between python script or event monitor for the software implementation. Access to the embedded ‘Python Easy Script’ gives the developer the ability to program complex control sequences. Using the virtual internal AT serial port, a Python script can be written to receive the asynchronous messages generated by the embedded DTMF decoder, interpret them, make decisions or execute commands.
If avoiding software programming is preferred, the user can take advantage of the event monitor. This feature allows a DTMF tone detection to be automatically associated with a specific action at the module by simply sending it an AT configuration command.
SMS at run
Telit modules also makes available, with no change in hardware configuration, one additional solution: the use of the ‘Embedded SMS AT Run’. This feature allows users to run AT commands remotely just by sending an SMS to the module. Responses and errors are sent back by the module via SMS. Two types of messages are available: simple and protected.
Protected messages are encrypted with an MD5 hash algorithm. It is important to note that the SMS AT Run feature is also available via TCP where AT commands are sent to the module via TCP/IP. Responses and IP protocol related traffic are redirected via TCP/IP to the device acting as the TCP terminal.
Event monitor example
Based on a Telit GL865 module, a simple 2 IN/2 OUT remote control can be implemented using the event monitor for action control. In this sample application the objective is to read the status of the two opto-isolated inputs or set the status of the two relays. If the user wants to link the activation of Relay 1 (connected to GPIO3) to the receiving of a DTMF tone equal to 0, the following custom command must be sent to configure the module: AT#EVMONI.
Upon detection of a DTMF tone 0, an event will be generated and AT#GPIO command will be executed automatically, activating Relay 1 (Figure 4). Contextually the module can be triggered by a HIGH level on GPIO1 and send an SMS to alert the remote application (Figure 5).



© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved