

Manufacturers of electronic equipment, including mobile phones, are working hard to develop products with originality and multifunctionality in order to maintain their competitive edge. Based on this background, one of the important demands for electronic components is miniaturisation.
Miniaturisation of electronic components enables higher-density mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs) in the equipment, and this ultimately leads to better performance and expanded functionality. Naturally, antennas are no exception to this demand.
Murata believes that miniaturisation of antennas is a necessary challenge for an antenna manufacturer. Another challenge is the caution required for adjusting the frequency characteristics, such as resonant frequency and frequency bandwidth, which are specific requirements for each antenna product. This is because even if optimal frequency characteristics are obtained when a discrete antenna is evaluated, these characteristics often change and no longer conform to the required specifications when the antenna is actually assembled into the final product.
There are several reasons why the frequency characteristics of an antenna change. For example, when an antenna is mounted on a PCB, the frequency characteristics change significantly depending on whether or not the ground plane is present immediately under the antenna. Furthermore, when a high-profile electronic component is placed in the neighbourhood of the antenna’s location, it can become a cause for change in the antenna’s frequency characteristics. Obviously, a gap between the antenna and the housing or housing material has a considerable effect on the frequency characteristics of the antenna as well.
For these reasons, in many cases, an antenna to be installed in portable electronic equipment is custom-designed to meet design specifications. Custom-designed products, however, have a downside, in that there is less flexibility in being able to change the electronic equipment design. If the frequency characteristics of an antenna change and no longer conform to the required characteristics because of the design change of the equipment, the prototype custom-designed antenna must be manufactured again. If the time to launch an antenna product into the market is delayed due to redesigning the antenna or to making another prototype, it could cause fatal damage to the production of the end product.
In addition to custom-designed antennas, Murata has developed antennas that enable electronic equipment manufacturers to freely set the required frequency characteristics themselves in order to quickly and flexibly respond to their individual requirements. The advantage of this type of antenna is that it can be adjusted to the required frequency characteristics by simply changing the characteristic value of a chip component that is externally attached to the antenna, without replacing the antenna itself. The newly developed LDA21_K series chip dielectric antenna has this advantage, while achieving size and profile reduction to meet market demands.
Designed to be the industry’s smallest antenna for the 2,4 GHz band (2,0 x 1,25 x 1,0 mm), the antenna is connected to a PCB after removing the ground from the chip antenna placement location on the back of the PCB. It requires a minimum mounting footprint of 3 x 5 mm², which is the industry’s smallest for a chip antenna. While achieving characteristics equivalent to the company’s conventional product, its size and PCB footprint have been reduced to approximately 40% and 35%, respectively, compared to the conventional product.
The LDA21_K series uses dielectric material with a high specific dielectric constant made from Murata’s original ceramics. Its structural design applies multilayer technology, which is one of Murata’s strong points, and the optimised antenna design makes the most of simulation technology and years of accumulated know-how on antennas.
These features made it possible to reduce the antenna size and the footprint size of previous products, while achieving equivalent performance characteristics. The LDA21_K series also offers the advantage of low cost compared to conventional product thanks to the size reduction.
For frequency adjustment, the chip antennas allow users to change the characteristic values of an external chip element as in the case of conventional products, as well as to select from five types of antennas with different resonant frequencies that are provided to cope with wider frequency changes. In this way, users can select a model suitable for the external environment.
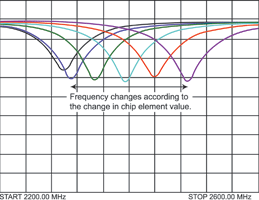
At first, a stripline is placed from the antenna to the ground plane. Next, the optimal model is selected from five types to roughly adjust the resonance frequency. Then, the chip element is connected to the stripline in series for fine adjustment. By installing a chip element with different element values, fine adjustment of the antenna resonance frequency is performed by means of the change in frequency.
Murata has application data on the detailed methods for designing a stripline and on the methods for adjusting the frequency using a chip element. Application data is also readily available.
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved