
Infineon Technologies has joined forces with TDK to develop an integrated solution for inverters to be used in e-mobility powertrains and industrial applications. The design enables developers to test and implement drive concepts quickly and easily. Asynchronous motors are used in the majority of electrical drives for industrial applications, while automotive drives employ synchronous motors with permanent magnets. For both automotive and industrial applications, the manufacturers limit these motors to a maximum permissible voltage rise (dv/dt) at the inverter terminals of about 5 kV/µs (according to IEC 60034-18-41).
The reason for this limit is the dielectric strength of the windings. When these motors are driven by an inverter, high earth leakage currents occur that are caused by parasitic capacitance in the windings in combination with the dv/dt of the inverter. These currents can lead to sparking in the bearings, cause surface erosion and therefore severely limit the service life of the bearings.
In order to achieve high energy efficiency, the power semiconductors of the inverters are operated at switching frequencies in the range between 4 kHz and 15 kHz. Due to the necessary slew rate and switching frequencies, this results in harmonics with a high amplitude in the frequency range around 1 MHz. In automotive applications, in particular, the power drive causes significant interference in the MW band (526,5 kHz to 1606,5 kHz), making MW reception nearly impossible in a car, for example.
New development delivers significant improvements
To be able to create an inverter that is gentle on the motor and that is electromagnetically compatible, Infineon and TDK have redeveloped the key components and matched them perfectly with each other, thus improving on the existing HybridPACK 1.
Apart from using the latest IGBT3 chip generation with a dielectric strength of 705 V, it now features six DC terminals on the HybridPACK module instead of the previous two (Figure 1).

In combination with the modified Epcos DC link capacitor, this enabled the ESL in the DC link to be almost halved from typically 30 nH to about 15 nH. The over-voltage generated when switching off the IGBT at the rated current (400 A) is correspondingly reduced by a significant amount: from 500 V to 420 V (Figure 2).
Together with the busbar to the DC link capacitor, the four additional DC terminals enhance the current capability of the HybridPACK module. In this way the new HybridPACK1-DC6 module is designed for more efficient future IGBT technologies with higher current capabilities. The power capability of existing applications based on the current HybridPACK1 with two DC terminals can be expanded easily with the HybridPACK1-DC6 because the new module has nearly the same dimensions as its predecessor. This provides good scalability for various xEV applications.
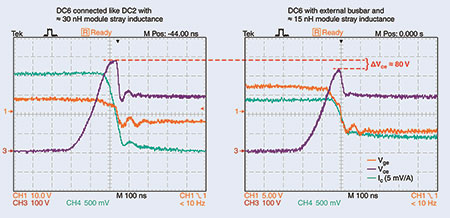
HybridPACK1 with its two DC terminals features a very compact design thanks to its integrated busbar. This feature was retained in the new HybridPACK1-DC6 for compatibility reasons. The external busbar to the Epcos DC link capacitor allows the DC supply current to be better distributed, thus achieving a better utilisation of the module. Figure 2 shows the current flow through the internal busbar at a rated current of 400 A. It represents a symmetrical distribution of the current between the busbar of the Epcos DC link capacitor and that of the module.
Epcos DC link capacitors prevent noise in the DC link
A further new development is the Epcos B25655P4477J DC link capacitor. Its terminals are designed to fit precisely with the DC terminals of the IGBT module. This is a further development of the existing Epcos capacitors that were designed for the HybridPACK and EASY series from Infineon.

The capacitor has a capacitance of 470 µF and is available with rated voltages of 450 V or 500 V d.c. It features dimensions of just 154 x 72 x 50 mm. The basis of this space-saving design is power capacitor chip (PCC) technology, which employs a stacked film to achieve a volume fill factor of nearly one for the capacitor housing. There is also a flat winding version with 380 µF (B25655P4387J), which is the most economical type. Both types are available with or without direct connection to an EMC filter.
High EMC performance despite unshielded cable
TDK has also developed a series of twin-conductor, high-voltage DC filters specially tailored to the demands of electric drives for vehicles. They thus ensure the fulfilment of all EMC requirements according to UN ECE Regulation No. 10 – Rev. 5.

The P100316* series of Epcos high-voltage DC filters (Figure 4) are designed for a maximum voltage of 600 V d.c. and thus correspond to the typical voltages that are supplied by high-voltage batteries. The current capabilities of the filters are around 150 A or 350 A d.c., which means that even drive systems with outputs of up to around 100 kW can be filtered. The DC resistance is only 0,05 m for all types, which means that there are no significant losses, even in the case of high currents.
The efficiency of the filters is so great that there is no longer any need for the usual shielded cables between battery and inverter (Figure 5). This not only has advantages in terms of cost and weight, but also ensures greater long-term stability as the expensive and fault-prone shielding connection can be dispensed with.
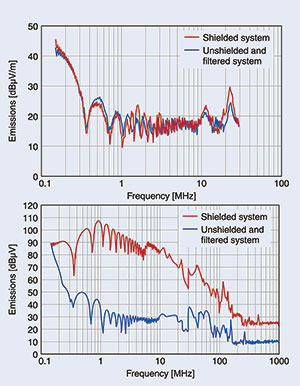
Despite using an unshielded DC cable, use of the Epcos HV DC EMC filter reduces the conducted interference in particular by up to 70 dB, which is equivalent to a factor of 3000. The new filters also enable a considerable reduction in the number of conventional EMC measures necessary for the individual system components.
Apart from outstanding electrical values, the filters are also impressive for their low weight and compact dimensions – technical parameters that are essential for their use in vehicles. Depending on the type, these dimensions typically range between 186 x 65 x 65 mm and 121 x 52 x 52 mm. Apart from the versions with a general common-mode rejection ratio, types are also available that exhibit a particularly high filtering effect in the long-wave spectrum between 150 kHz and 300 kHz.
Epcos ferrite cores increase the service life of motors
At the output of the inverter, the steep pulse edges cause voltage spikes that can be further exaggerated by parasitic inductances of the motor cables. Under unfavourable conditions these voltage spikes can result in arcing that could destroy the motor windings. At the same time, the switching frequency of the inverter leads to a higher parasitic capacitive load between the windings of the motor and its housing (ground potential). This results in leakage currents that can flow through the motor bearing and thus cause sparking.
One remedy for this is provided by ferrite ring cores, through which the motor cables are routed at the output of the inverter. Thanks to the lower dv/dt, this likewise significantly can reduce common-mode interference significantly and lower leakage currents to a non-critical level, which ensures that the limits of Classes I through III are adhered to (Figure 6).
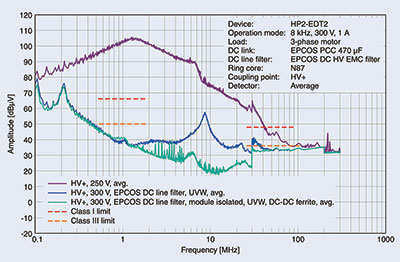
For this purpose, TDK offers a broad spectrum of ring cores from the B64290L* series in various dimensions and ferrite materials, which are optimised for certain frequency ranges and temperatures, and can therefore be tailored to any drive system. Ferrite materials such as T65, N30, N87, which are also used for Epcos EMC chokes, are recommended for this purpose.
In addition, Infineon developed a new driver board for the HybridPACK1 DC6 module, which is based on the proven 1ED020I12FA2 series of Infineon gate driver ICs. The board ensures efficient EMC compatible operation and enables the benefits of this improved configuration to be easily implemented. The result is the first power output stage consisting of an IGBT module, DC link capacitor, EMC filter and gate driver, and in which all necessary EMC requirements are considered right from the beginning.
For more information contact Frank Holzberg, Electrocomp, +27 (0)11 458 9000, [email protected], www.electrocomp.co.za
| Tel: | +27 11 458 9000 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.electrocomp.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Electrocomp |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved