
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a highly versatile active remote sensing technique that is used in Earth and atmospheric sciences, autonomous vehicles, urban planning, and many other applications. Some of the most important components of LIDAR sensors are the filters that isolate target signals, while preventing sunlight and other extraneous light from reaching the detector.
A wide variety of applications and sensor types exist, from laser altimeters to Raman LIDAR systems, all with different return signal strengths and LIDAR filter requirements. Therefore, LIDAR filters must be designed with the specific application and sensor type in mind to maximise signal-to-noise ratio.
Laser altimeters and other LIDAR sensors scan a pulsed laser across the environment and determine the return time of the reflected signals by calculating the precise position and orientation of the sensor as the signals are emitted and received. To accomplish this, a LIDAR system requires five basic components: a laser, either a mechanical or software-based scanning system, a receiver or photodetector, a GPS unit, and a high-precision clock. Aerial LIDAR systems also require an inertial measurement unit (IMU) to determine orientation.
The basic equation used to determine the distance between the object and the sensor is:
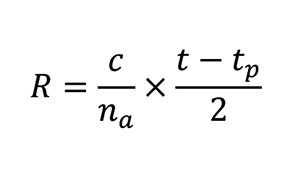
Where R is the range in metres, c is the speed of light, na is the index of refraction of air, t is the time when the signal returns, and tp is the time when the pulse is emitted.
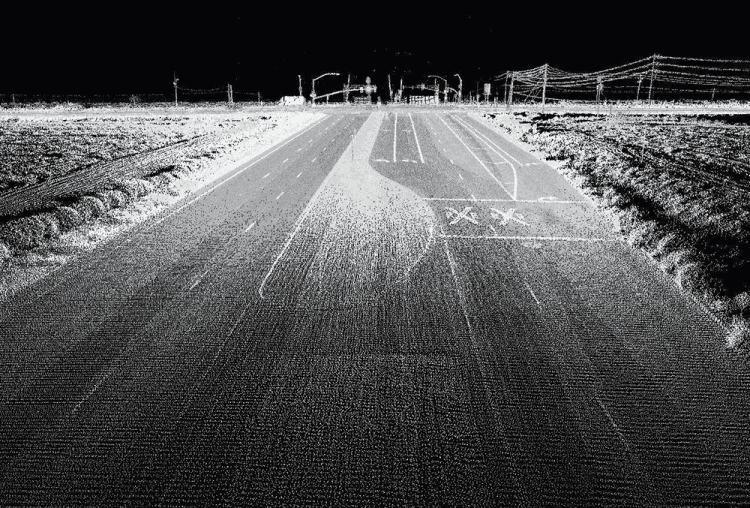
If a single LIDAR pulse only encounters one object, such as bare ground, the result will be a single corresponding return signal. However, since the beam is generally expanded as it is emitted, multiple objects such as tree branches and shrubs can be encountered before the signal reaches the ground, resulting in multiple reflected signals. Depending on the associated software, LIDAR systems will either record these returns as discrete points, or will display the data as a waveform showing each return as a function of time (Figure 1). The result is a data point cloud that can be used to create high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) or 3D images of features in the surrounding environment (Figure 2).

LIDAR filters
Although return signals can be isolated using a variety of different filtering technologies, most LIDAR systems employ thin-film interference filters because of their inherent durability and lack of a need for maintenance or calibration. This is an important consideration because many LIDAR sensors are mounted to satellites, aeroplanes, UAVs, autonomous vehicles, and other platforms that require the sensor to function under harsh environmental conditions, with little to no maintenance.
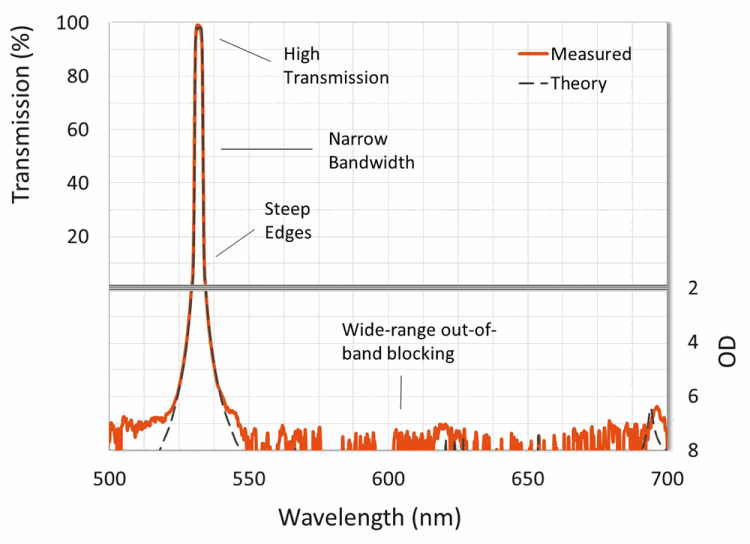
Because of the precise nature of LIDAR return signals, most LIDAR filters are ultra-narrowband thin-film interference filters. These filters must be able to achieve both high transmission over an ultra-narrow bandwidth to isolate the return signal, and deep out-of-band blocking over a large wavelength range to attenuate sunlight and other extraneous light (Figure 3). However, there are many different types of LIDAR systems that each necessarily demand application-specific filter requirements to maximise signal-to-noise ratios.
Laser altimeters, for example, typically require ultra-narrowband interference filters to be less than 1,5 nm at full-width half maximum (FWHM), while achieving over 90% transmission at the laser wavelength and greater than OD6 (-60dB or 0,0001% transmission) out-of-band blocking from
LIDAR systems also require that the filters’ thin-film coating must be as uniform as possible. When uniformity is not controlled, the thin-film layer thicknesses vary across the surface of the filter, resulting in a location-dependent wavelength shift of the filter spectrum across the clear aperture. If a filter with uncontrolled uniformity is integrated into a LIDAR system, a large number of LIDAR return signals will end up being blocked by the filter and will not reach the detector. Fortunately, a uniformity-controlled thin-film coating will ensure that target signals will not be blocked by the filter (Figure 4).
In addition, LIDAR filters must also be designed with the sensor platform and environmental conditions in mind. Aerial- and ground-based LIDAR systems operate at temperatures that can range from -40 to 105°C, while satellite LIDAR operating ranges depend on the orbit and thermal control system of the satellite. Therefore, any interference filters integrated into systems that operate at extreme temperatures should be designed to minimise temperature-dependent wavelength shift.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved