
Wi-Fi is a universally accepted, highly familiar and cost-effective technology for connecting devices of all types wirelessly. The familiarity originates from users’ adoption of the technology for PC, tablet and mobile device connectivity and Wi-Fi connectivity is ubiquitous in homes and workplaces across the globe. The ability to establish a network without service provider input and enable local connectivity at very low cost in comparison to cellular connectivity is a compelling attraction.
The technology’s appeal has widened as Wi-Fi networks have become ubiquitous across city centres, industrial and enterprise campuses and sites such as hospitals, ports, and entertainment venues. Innovations such as Wi-Fi 6 and 6E Wi-Fi 7 and Wi-Fi HaLow are expanding the applicability of Wi-Fi to use cases that need higher speeds, wider coverage and lower latency and positioning Wi-Fi, as a compelling alternative to cellular connections.
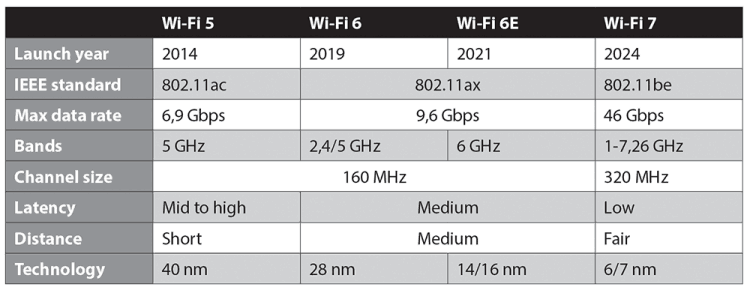
Each of these new variants presents different incentives for the market to move beyond Wi-Fi 5. The transition to Wi-Fi 6/6E has been primarily driven by the need for higher efficiency, better performance in dense environments, and improved power management. Wi-Fi 6 and 6E promise better coverage, improved node density and lower power consumption.
Wi-Fi 7 also includes these benefits and adds better interference resiliency and, most importantly, low latency for applications such as augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), industrial automation and cloud gaming. Wi-Fi 7 also introduces multi-link operation (MLO) and lower latency, a game-changing feature that allows devices to transmit and receive data across multiple frequency bands simultaneously. This significantly reduces network congestion and improves reliability, especially in environments with high interference.
In addition, enhancements in WPA3 security across Wi-Fi 6 and 7 ensure stronger encryption and protection against cyber threats, making these technologies a secure choice for enterprise and industrial applications. The advances introduced across Wi-Fi 6 and 7 ensure that Wi-Fi continues to meet the growing demand for seamless, high speed connectivity in an increasingly digital world.
Unlike traditional Wi-Fi technologies, Wi-Fi HaLow adds a further dimension to the applicability of Wi-Fi. HaLow operates in the sub-1 GHz spectrum band, offering extended range and better penetration through walls and obstacles. This makes it particularly suitable for IoT applications such as smart agriculture, industrial automation and smart cities, where low-power, long-range connectivity is essential. By enabling connectivity over distances of several kilometres, HaLow fills a crucial gap in the IoT ecosystem.
Quectel’s strong portfolio of Wi-Fi solutions includes the latest Wi-Fi 6, 7 and HaLow modules.
Wi-Fi 6
Quectel’s FGS060N, FCS962N-LP, FC66E and the FCM363X provide high efficiency and improved performance in dense networks.
The Quectel FGS060N is a high-performance Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.2 and 802.15.4 module that supports a maximum data rate of 600,4 Mbps. The module measures
The Quectel FCS962N-LP supports Wi-Fi 6 in the 2,4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands and Bluetooth 5.4, Bluetooth LE audio and BLE long range. Maximum data rate is 143,4 Mbps and the module has dimensions of
The Quectel FC66E is a Wi-Fi 6E and Bluetooth 5.3 module that supports a maximum data rate of 3000 Mbps. Measuring
Wi-Fi 7
Quectel’s FGE576Q and FME170Q-865 deliver ultra-fast network speeds, multi-link operation and optimised network efficiency.
The Quectel FGE576Q supports Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth 5.3, enabling dual-band simultaneous operation on 2,4 GHz + 5 GHz and 2,4 GHz and 6 GHz. The module offers a maximum data rate of 3,6 Gbps and supports ultra-low latency for real-time response. The module is ideal for cloud gaming, 8K audiovisual streaming, augmented and virtual reality use cases, Industrial IoT and telemedicine.
The Quectel FME170Q-865 is an ultra-low latency Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth 5.4 module, offering a maximum data rate of 5,8 Gbps. It supports simultaneous operation on 2,4 GHz + 5 GHz, 2,4 GHz + 6 GHz, 5 GHz + 5 GHz and 5 GHz + 6 GHz bands.
Wi-Fi HaLow
Quectel’s FGH100M-H is ideal for long-range, low power IoT applications that require connectivity over kilometres. With a maximum data rate of 32,5 Mbps, the module operates in the Sub-1 GHz range, enabling users to control devices within a radius of 1 km. The module can enable simultaneous access for up to 8191 devices on the same Wi-Fi access point.
To read the complete white paper visit www.dataweek.co.za/ex/Q_WiFi.pdf
| Tel: | +27 11 781 2029 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.icorptechnologies.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about iCorp Technologies |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved