
In any system, what is the weakest link? If you’re designing for any kind of harsh environment, it may well be the humble connector. That holds true for any application that needs rugged components, whether it’s industrial, mining, transportation, or anything else. In safety-critical systems, any failure can be serious – and potentially fatal.

Connectors are an essential part of any design, whether that is handling analog signals, digital data or power. In many systems, there will be multiple sensors and actuators that must be connected, as well as several sub-systems.
In this article, we’ll look at the environmental factors that can cause connector failure, the different kinds of connector that can survive tough conditions (including the relevant IP ratings), and how you can choose the right connectors for your application – without wasting space and cost by over-specifying.
Protecting against dust and moisture
One of the most likely causes of connector failure is the ingress of moisture or contaminants, such as dust or dirt. Water can get into connectors from the weather, or from cleaning with a hosepipe or other source of flowing water. Cleaning can also introduce chemicals or surfactants, which can corrode electrical conductors, thus at the very least decreasing their ability to carry current, and possibly causing failures.
Moisture can also result from condensation in humid environments, particularly when a device is moved from a cold to a warm environment. Inevitably, water and electricity don’t play nice together – and the result can be damaging short circuits.
Dirt or dust that finds its way into a connector can build up over time to form an insulating layer, which can mean there is a poor quality connection made by a connector. The dust or dirt can also cause overheating.
Ingress protection, or IP, is described by the IEC’s IP standard, IEC 605029, which has become widely used today. This standard uses a two-digit number to show a device’s protection against solid objects (first digit) and liquids (second digit), as shown in Table 1.
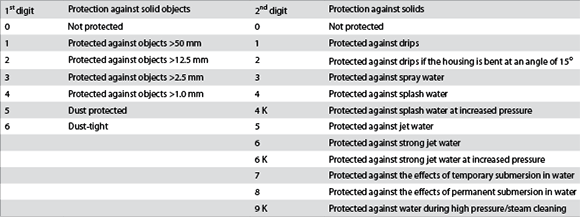
For example, IP67 means a device is fully dust-tight and protected against temporary immersion in water. Such protection is achieved with heavy-duty seals and grommets, often made from silicone. Multiple seals can provide redundancy, so ingress protection is maintained even if one seal fails.
As well as the IEC IP rating, another commonly used system for ingress protection is the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) ratings. Both the IP and NEMA ratings are usually provided in product data for connectors and enclosures.
Other environmental hazards
In addition to dust and moisture, extremes in temperature can be damaging to connectors – such as the high temperatures experienced in many industrial processes, or in mining, where high ambient temperatures underground contribute to extremes experienced by connectors. Frequent cycling of temperatures from low to high, which is likely to occur in many applications, also causes problems.

In sub-zero temperatures, there is also the issue of ice to deal with. As water freezes, it expands, which can result in large forces, possibly damaging connectors and cables. The extra weight of ice can also put strain on connectors. When specifying connectors, look for an extended temperature range. For example, for fibre-optic cables, Molex’s LC2 metallic optical connectors (Figure 1) use a metal body that can handle high temperatures up to 150°C.
Connectors can also suffer physical damage, whether that is from an impact or from the effect of vibration – which can cause mechanical failure or damage to electrical connections. All-metal bodies can provide the strength to withstand impacts, while thermoplastic shells will resist corrosion, as well as being flame- and chemical-resistant.
Metal construction can also ensure a connector provides sufficient protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Another area of mechanical design to consider is strain relief, which ensures any forces applied to the cable or exterior of the connector cannot be passed on to the electrical connection – many connectors provide strain relief as standard.

Suitably rugged connectors will provide the ability to handle vibration, which is defined by standards such as MIL-STD-202. For example, the CeeLok FAS-T Gigabit Ethernet connectors from TE Connectivity (Figure 2) can cope with high degrees of vibration, as well as being IP67-rated and having an operating temperature range of -65°C to +175°C.
Picking the right connector
When choosing a connector, it goes without saying that the first step is to understand the target application and the likely environmental conditions. Plan for the worst case, so you know your connector can withstand whatever is thrown at it.
Once you know what you’re aiming for, any necessary approvals, such as IP67, should be checked on the connector’s datasheet, which will also state the operational temperature range. Also consider any other standards that are required, for example in South Africa, the South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) has developed multiple standards that relate to connectors.
Look for connectors with a secure locking mechanism that can withstand vibration, and that provides confirmation that it is engaged, with an audible noise or tactile response. There are many types of locking method, so make sure you pick one that is appropriate – including planning for how often it will be disconnected and connected in its lifetime. Secondary locks, commonly referred to as wedgelocks, will ensure that contacts are held firmly together.
Picking components that have been tested following a relevant standard, such as MIL-STD-202, is important, to ensure they provide the required robustness over their full lifetime. The standards-based tests use techniques such as ‘highly accelerated life tests’ (HALT) to accurately simulate real-world conditions, and thus ensure product reliability.
On the other hand, do make sure you don’t go too far. The temptation is to over-specify your connectors, but this can mean unneeded costs and space wasted by bulky parts. You may be tempted by the connector with the highest IP rating, when a lower rating is sufficient and cheaper. Similarly, a plastic connector may well be preferable to a more expensive metal connector.
Conclusion
While connectors are sometimes left to last in a system design, they are essential components, and you need to get their selection right. When all the possible permutations are considered, there is a huge range of options, and your best option may well be talking to a distributor who can provide expert technical advice.
For more information on harsh environments, as well as listings of thousands of products and their IP ratings, see www.mouser.co.za/applications/harsh-environment-technology/
For more information contact TRX Electronics, authorised Mouser independent representative in South Africa, +27 12 997 0509, [email protected], www.trxe.com
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.trxe.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about TRX Electronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved