
Microcontrollers have I/O lines for user applications. Sometimes these lines can be used either as I/O or bus, depending on the memory location. If the microcontroller is a ROMless device, instructions are fetched outside the device and as the bus is always there, an emulator can be built around it. The main issue is how to emulate a microcontroller in ROM mode, which means when the instructions are fetched inside the chip memory and the I/O lines remain unchanged until a related instruction that affects them is executed. ROM is now not necessarily a Read Only Memory, but it can also be a device with Flash technology, meaning a memory that holds the user code without being erased while power goes down.
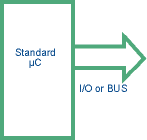
Bond-outs
Emulators need access to the internal bus especially when the bus signals are shared with I/O lines or when there is no external bus available at all. As a solution the silicon manufacturers used to produce bond-out chips which are the same microcontrollers mounted in a bigger package with more pins that provide the internal bus, status and control signals. I/O lines and the internal bus are accessible through different pins in the chip. Bond-outs are needed only for the emulator vendors.
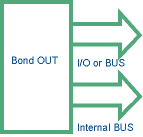
Emulation mode
A solution came a few years ago that consisted of multiplexing the I/O lines with the internal bus while entering the chip into a special emulation mode - an undocumented feature licensed only to emulator vendors. A pattern is sent to the standard chip through one of the pins while the microcontroller is reset. With the addition of external logic, I/O lines are sampled and reconstructed, while the internal bus is available on a different time slot. The major advantage of the emulation mode is that all the emulation functions are already implemented in the standard silicon, so with new versions of the chip also the emulators are automatically updated. This mode is also called 'Emulation Hooks'. I/O lines are fully reconstructed and the user has available all I/O features as in the actual devices.
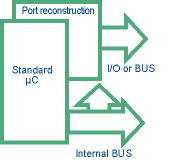
ROM and ROMless support
Some silicon vendors do not have any solution for emulators - this means their microcontrollers do not have Emulation Mode or available bond-outs. Therefore, there are a few solutions for emulation:
1. Use a similar chip from other vendor in the emulator. For the emulator it does not matter which is the memory technology (EPROM, Flash, etc) so for example a chip like 89C51 (Flash type) can be emulated by an 87C51 (EPROM type).
2. Use the chip in ROMless mode. In this case the emulator may have placed exactly the same silicon as the final design. Nevertheless, the chip will work in ROMless mode. This is not a problem in some cases. For example if the device is an 8051 derivative and the user code executes MOVX instructions to access data outside the microcontroller, activating Port 0 and 2 as buses, a ROMless type can be used because in any case port contents are changed.
Low pin count microcontrollers
Sometimes these devices can be emulated using a similar device with standard pinout and a socket converter. For example most of the 20-pin devices have a 40-pin superset with all the same functionality and more. This may not solve all the problems because the small devices may also have pins with dedicated functions not available in any other device.
Flash microcontrollers
The Flash technology is now being added to all new microcontrollers to implement the code memory. Flash technology includes ISP and IAP. The ISP (in-system programming) allows loading the user code without removing the chip from the target circuit. The IAP (in-application programming) may be used to let the code to modify itself without affecting I/O lines or activating a bus, and this is also a very basic need of emulators.
All the available emulators work in emulation mode or using bond-outs or in ROMless mode, thus allowing access to the internal buses. Therefore, the actual code is in the emulator overlay RAM memory and not in the microcontroller Flash. So, ISP or IAP is never used by the emulators. This is a problem for many users that want to emulate these features. Ceibo developed a new technology that is being implemented by several silicon vendors, which with the addition of a few internal registers inside the microcontroller, all the basic emulation functions are already inside the chip. These capabilities are trace memory, breakpoints, code downloading, register modifications and others. The FE-xxxx series of emulators is now available for microcontrollers produced by Atmel M&W, Dallas Semiconductors, Winbond and Philips. Some others will be added soon.
| Tel: | +27 11 887 7879 |
| Email: | [email protected] , [email protected] |
| www: | |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Sivan Electronic Supplies |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved