
For a power supply to function reliably, there must always be an input voltage within the permissible range available to the switching regulator.
A power supply’s source, in actual use, is never ideal. The real behaviour, including parasitics, needs to be considered to build a reliable power system. When we use power supplies, we ensure that a DC-DC converter, such as a switching regulator, can withstand a certain input voltage range and that it can generate the required output voltage from it with sufficient current.
The input voltage is frequently specified as a range because it is usually not regulated precisely. For a power supply to function reliably, however, there must always be an input voltage within the permissible range available to the switching regulator. For example, a typical input voltage range for a 12 V supply voltage may lie between 8 V and 16 V. Figure 1 shows a step-down converter (buck topology) that generates 3,3 V from a nominal voltage of 12 V.
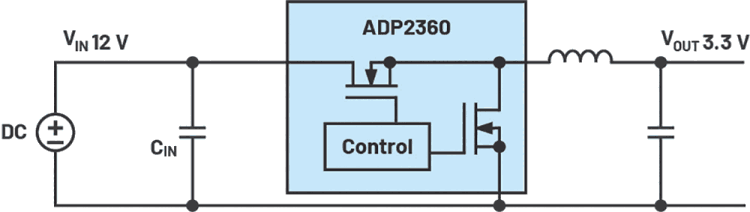
However, when designing the DC-DC converter, it is not sufficient to only consider the minimum and maximum input voltage values. Figure 1 shows that the buck converter has a switch at its positive input. This switch is turned on or off. The switching speed should be as high as possible so that only low switching losses occur. However, this causes a pulsed current to flow on the supply line. Not every voltage source can deliver these pulsed currents without any problems. As a result, voltage drops occur at the input of the switching regulator. To minimise this, backup capacitors are required right at the input of the power supply. Such a capacitor is shown as CIN in Figure 1.
Figure 2 shows the circuit from Figure 1, but this time with the parasitic elements of the supply line and the voltage source itself. Both the internal resistance of the voltage source (RSERIES), the inductance and resistance of the supply line (R, L supply line) and any current limitation are key characteristics of the voltage source that must be taken into account to guarantee trouble-free operation of the switching regulator.
For the most part, the correct selection of the input capacitors can ensure proper operation of the circuit. The first approach should be to take the recommended capacitance value for CIN from the data sheet for a switching regulator IC. However, if the voltage source or the supply line exhibits special characteristics, it makes sense to simulate the combination of the voltage source and the switching regulator. Figure 3 shows a simulation performed with the LTspice simulation environment from Analog Devices.
A simulation circuit for the ADP2360 buck converter is shown in Figure 3. The simplified form, in which the input voltage (IN) is generated with an ideal voltage source, is shown here. Because no internal resistance is defined for the voltage source and no parasitic values are given for the supply line between the voltage source and the switching regulator, the defined voltage is always applied to the VIN pin of the ADP2360. Therefore, it is not necessary to add an input capacitor (CIN).
However, in the real world, an input capacitor is always required with a switching regulator because the voltage source and the supply line are not ideal. If a simulation environment such as LTspice is also used for checking the behaviour with different input capacitors, a voltage source with internal resistance and a supply line with parasitic values for resistance and inductance, as shown in Figure 2, must be used.
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved